-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Shanti Pokhrel, Rabin Bhandari, Dhana Ratna Shakya, Rupak Bhandari, Bijaya Gautam and Tarun Paudel*
Corresponding Author: Tarun Paudel, Prof. and HOD GP and Emergency medicine Gandaki Medical college, Nepal.
Received: August 25, 2024 ; Revised: January 25, 2025 ; Accepted: January 28, 2025 ; Available Online: February 17, 2025
Citation: Pokhrel S, Bhandari R, Shakya DR, Bhandari R, Gautam B, et al. (2025) Prevalence of Depression and Quality of Life of Patients with Chronic Headache. J Nurs Midwifery Res, 4(1): 1-14.
Copyrights: ©2025 Pokhrel S, Bhandari R, Shakya DR, Bhandari R, Gautam B, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Backgrounds: Headache is the symptoms of pain anywhere in the region of head or neck. Chronic headache is defined as the presence of headache more than 15 days per month for longer than 3 months. Frequent headache can affect the relationship, employment and other activities, with most migraine sufferers and around half of tension type headache sufferers reported limitation of activities, disability during a headache attack. Chronic headache is often associated with depression. There is high co-prevalence of migraine and depression. Chronic headache patient with depression showed reduced quality of life.
Objective: This study aimed to determine the prevalence of depression among patients presenting with chronic primary headache and to describe the quality of life in patients with chronic primary headache with depression and without depression.
Methods and Methodology: This is a descriptive cross-sectional study of 139 chronic primary headache patients at BPKIHS, Nepal from 2017 March to 2018 March among patient visiting GpOPD OF BPKIHS. Chronic primary headache defined by ICHD-3 criteria. Depression was assessed by BDI questionnaire and quality of life determined by WHOQOLBREF questionnaire. Consider sociodemographic, clinical, and individual variations that impact chronic headache patient.
Results: A total of 139 chronic headache patients visiting the general practice out patient’s department from March 2017 to March 2018 at B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences were included in the study. Prevalence of depression was 45.3% and mean value of BDI score with depression was (20 ± 5). The median (IQR) BDI score was 12 (6, 18, Q1, Q3). The median values showed significant difference among patients with depression and no depression. Mean QOL score were higher in the group without depression patients in comparison to the groups with depression.
Conclusion: Chronic headache is often associated with depression. The prevalence of depression in chronic headache patients in the present study was 45.3%. This study suggested that patients with chronic primary headache with depression had poor QOL as compared to patients without depression.
Keywords: Chronic headache, Depression, Quality of life
INTRODUCTION
Chronic headache is a common cause of human suffering and is common in general practice [1]. It is defined as the presence of headache more than 15 days per month for longer than 3 months [2-6]. However, it is commonly used as the headache which occurs repeatedly or persistently for a long period, including migraine, tension type headache and cluster headache as major disorders [2]. The most common chronic primary headache is chronic migraine headache, chronic tension type headache [7]. The headache prevalence ranges from 38% to 46% with more than 90% of general population suffering at least one attack of headache a year [8] where prevalence of chronic headache ranges from 1 to 3% [8,9]. According to the study from the same institute 1% of outpatient visits presented due to chronic headache [8]. The disability associated with this disorder is substantial and includes a diminished quality of life related to physical and mental health, as well as impaired physical, social and occupational functioning [9]. Depression is one of the most common psychiatric disorders and lifetime prevalence of depression is very high among women in the world (WHO 2000). Depression is a chronic relapsing organic brain disease, means onset is at 27years of age, however 40% of sufferers present by 20 years of age. Untreated depression can result in disability and death [10]. Chronic headache is often associated with depression [11-13]. Headache can affect the relationship, employment and other activities, with most of migraine sufferers and around half of tension type headache sufferers reported limitation of activities, disability during a headache attack [14]. There is high co-prevalence of headache and depression [15]. In a study from BPKIHS, 34% of psychiatry out patients with migraine headache had affective disorder, mainly depression [16,17]. Chronic headaches are widely spread all over the world and are associated with a wide range of medical and psychiatric co morbidities [18]. Chronic headache patient with depression showed reduced quality of life [19]. The bidirectional influences and strong interactions between headache and depression have been well‑documented, but mainly in chronic migraine and chronic tension type headache [20]. In contrast, more frequent migraines could directly lead to the presence of a depression, which is associated with more severe depression. Shared biological pathways and norepinephrine and serotonin neurotransmitters provide one possible explanation for the co‑occurrence and associations between pain and depressive disorders [21]. There is limited data regarding the prevalence of depression in primary chronic headache disorders in our set up. Thus, there is a need for further studies to report the prevalence of depression in primary chronic headache and to assess their quality of life.
METHOD AND METHODOLOGY
Study Design: This is a descriptive cross-sectional study.
Study setting: General practice out-patients department (GpOPD) of B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Science, Dharan, Sunsari district, Nepal.
Study population: Patients visiting GpOPD at B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Science with complain of chronic headache.
Sampling technique: Convenience sampling.
Duration of study: One year.
Sample size estimation:
According to Karin Zebenholzer [22]; prevalence of depressive symptoms in chronic headache was 43% P = 43 % (defined as HADS D more than 8)
Q= 57
Permissible error (L) = 20% of 43 = 8.6
Sample size (n) = (Z *2PQ) /L2
(1.96)2 X 57X 43 /8.6*2 = 127
Adding 10% for non-response, the final sample size will be (n) =139
n= Sample size.
Z= Standard error from the mean corresponding to 95% confidence level=1.96
P= 43% taken to be estimated prevalence of depression in chronic headache Zebenholzer [22].
L = Permissible error
The samples were taken from patients in GpOPD with complains of chronic headache at BPKIHS who met the inclusions criteria.
Inclusion Criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
Methodology
This is a descriptive, cross-sectional study. The purpose of the study and any ethical concerns were explained. A written consent was taken from the patient after they accepted to participate in the research. Thereafter, they were diagnosed according to the ICHD3 diagnostic criteria by open and close ended questions by the researcher. After that BDI questionnaire and WHOQOLBREF questionnaire were provided to chronic headache patients, data were collected by means of self-administered structured questionnaire, filled promptly and any queries regarding the questionnaire were explained by the researcher.
Data collection Instrument:
The headaches were classified according to explicit diagnostic criteria of ICHD-3, primary chronic headache is defined as headache at least 15 days per month for at least 3 months but in case of chronic cluster headache, chronic paroxysmal hemicranias, chronic SUNCT, chronic SUNA, headache should last for at least 1 year (International Headache Society 2013), not secondary to head trauma, brain tumor, infection, substance or its withdrawal etc., those are included in secondary headache.
Beck depression inventory (bdi): The Beck Depression Inventory is a widely used self-report measure of depression, requires approximately fifteen minutes to administer. The BDI was introduced in 1961. Beck derived the BDI from clinical observations and symptoms commonly seen in depressed patients from symptoms typically absent in those not depressed. Beck originally designed the BDI for patient assessment but it is now widely used as screening instrument. Current classification ranges for the BDI based on a University of Pennsylvania study are 0-13 for no depression, 14-19 for mild, 20-28 for moderate and 29-63 for severe [23]. It has been validated in Nepal too [24].
Whoqol-bref: The WHOQOL-BREF contains 2 items from the overall quality of life and general health, and one item from each of the remaining 24 facets included in the WHOQOL-100. Recent analysis of the WHOQOL-100 structure has suggested the possibility of merging domains 1 and 3, and also merging domains 2 and 6, thereby creating four domains of quality of life. In our current approach to scoring the WHOQOL-BREF, these domains have been merged therefore and four major domains are assessed: physical, psychological, social relationships and environment. One of the study from Nepal validated WHOQOL-BREF questionnaire, scoring as [25,26].
Statistical analysis: The data obtained from each participant was recorded in the proforma sheet and the data was entered into Microsoft Excel sheet and transferred into Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) - 11.5 versions. The analysis of the data was done in SPSS. For Descriptive statistics was completed with frequency, percentage, proportion, mean, standard deviation, inter-quartile range. For graphical representation bar diagram, boxplot, scatter line was constructed. Non-parametric kruskal wallis test and Chi square test was used to find out association between two categorical variables where p value was considered significant as 0.05. ANOVA test, Pearson correlation test was used to compare the mean to find out the QOL and to determine the correlation between depression and QOL, where p value was considered significant as 0.01. Ethical clearance was obtained from the Institutional ethical review board of BPKIHS.
RESULT
A total of 139 chronic headache patients visiting the general practice out patient’s department from September 2017 to September 2018 at B.P. Koirala Institute of Health Sciences were included in the study. Sociodemographic characteristics of chronic headache patients.
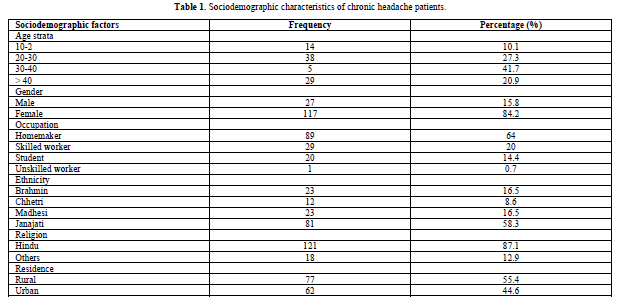
The patient’s mean age (± SD) was 34.37 (± 8.886) with a female: male ratio of 4.33. Majority were Homemaker (89%) by occupation, Janajati (58.3%) by ehnic group, Hindu (87.1%) by religion. Majority of patients were from rural area (55.4%) (Table 1)
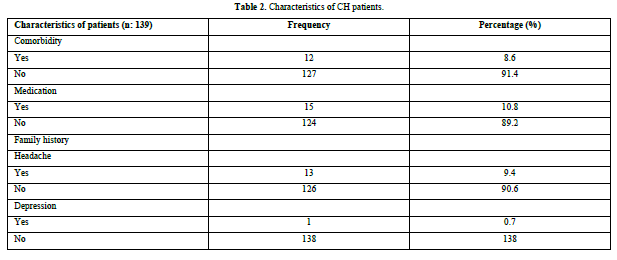
Among 139 CH patients, hypertension and hypothyroidism were found as a comorbidity. (5.7%) were on Antihypertensive, (2.8%) were on Thyroxine, and (2.3%) were under Antidepressive. Family history of headache was present in (9.4%). Family history of depression was present in (0.7%) (Table 2).
Headache Characteristics
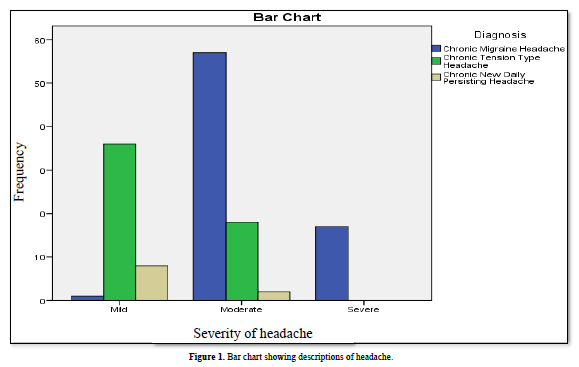
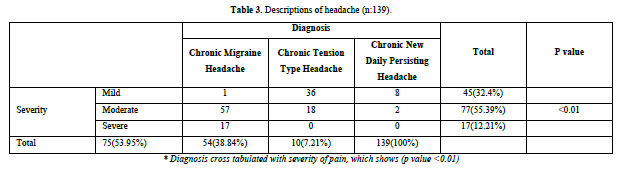
Among 139 CH patients, chronic migraine headache was commonest type of headache (53.95%). More than half of patients (55.39%) reported moderate severity of pain. Only (12.2%) had severe pain (Figure 1 & Table 3). The mean frequency of headache per month was (17.39 ± 4.18). The mean duration of headache in years was (5.36 ± 4.79).
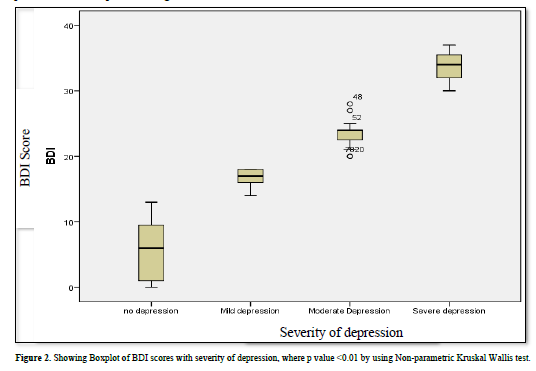
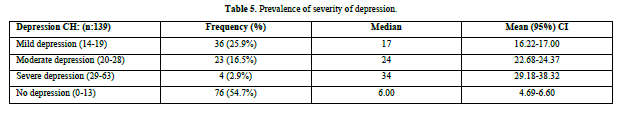
The median (IQR) BDI score was 12 (6, 18, Q1, Q3). The median values showed significant difference among patients with depression and no depression (Figure 2). Most of the chronic headache patients had mild depression (25.9%), followed by moderate (16.5%), and severe depression (2.9%) (Table 5).
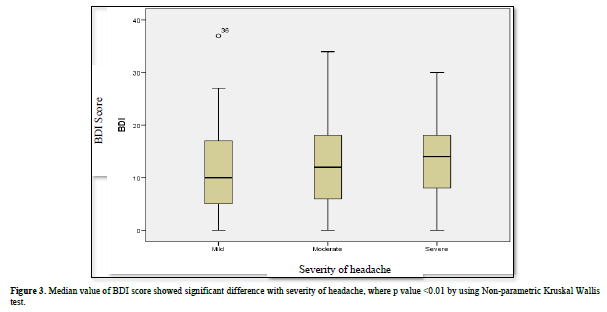
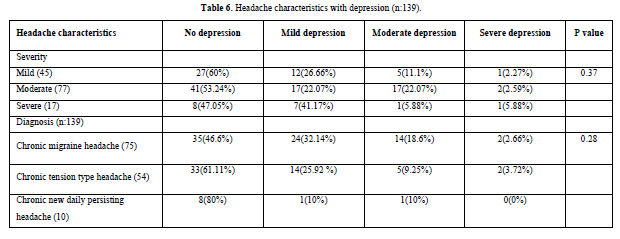
Depression reported more on severe headache (52.93%), followed by moderate (46.63%) and mild headache (40%). Depression most commonly seen in chronic migraine headache patients (49.53%), followed by chronic tension type headache (38.89%), and chronic new daily persisting headache (20%) (Figures 3 & 4 and Table 6).

Severity of depression cross tabulated with severity of headache and diagnosis, did not show statistical significance (P value calculated by Pearson chi-square).
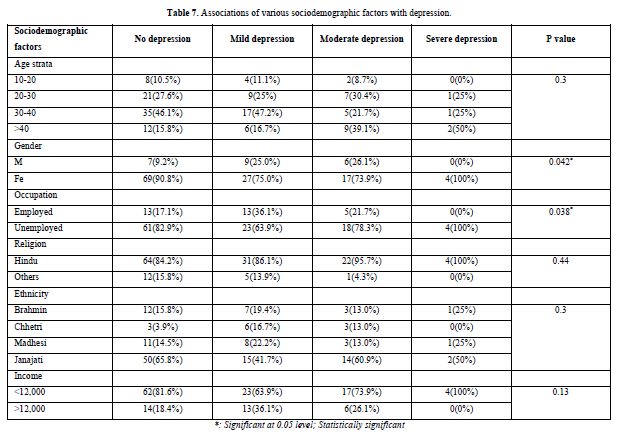
Severity of depression were cross tabulated with age, sex, occupations, religion, ethnicity, income. Age and occupation showed statistical significance when compared with severity of depression. Female (48/139), Unemployed (45/139), Poor (44/139), Hindu (57/139), Janajati (31/139) chronic headache patients had more depression (Table 7).
QOL in chronic headache patients with depression and without depression.
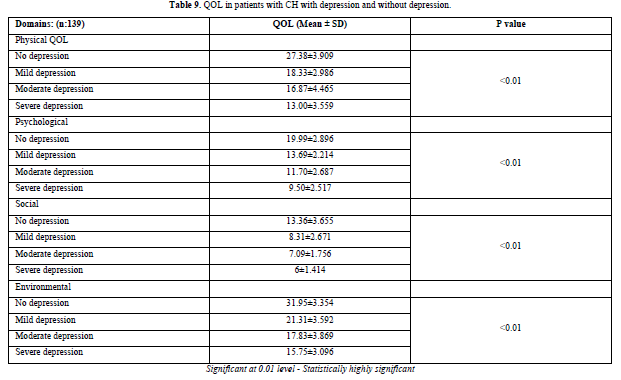
Mean QOL score were higher in the group without depression patients in comparison to the groups with depression. Significant difference among the group (p value< 0.01) was evidenced by the independent samples T- test (Table 8).

Mean QOL score were higher in the group with no depression patients in comparison to the groups with mild to severe depression. Significant difference among the group (p value < 0.01) was evidenced by the ANOVA test (Table 9).
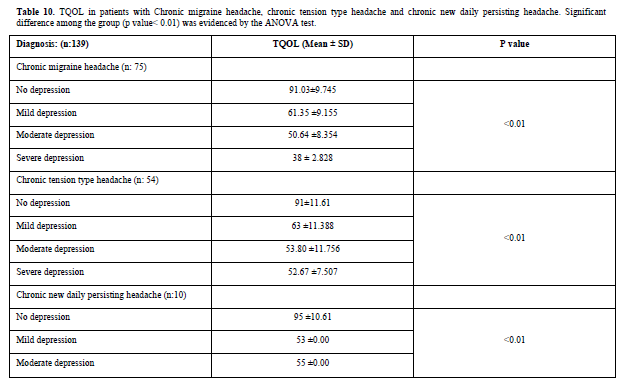
Mean of TQOL score were higher in the group with chronic migraine headache with no depression patients in comparison to the groups with mild to severe depression (Table 10).
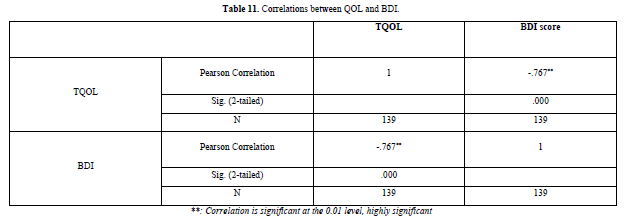
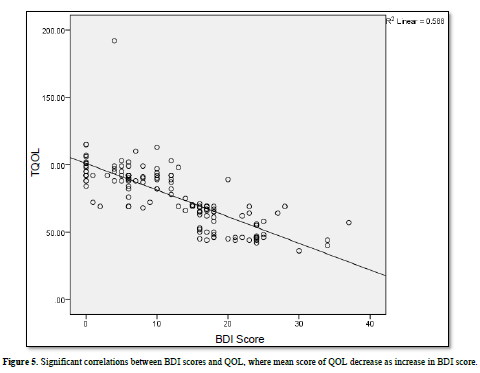
There were significant correlations between QOL and BDI, evidenced by Pearson correlations test (P value < 0.01) (Table 11 & Figure 5).
DISCUSSION
Chronic headache is one of the most common neurological disorders and accounts for multiple visits to the general physician and neurologist [27]. Chronic headaches cause significant disability with reduced efficiency, poor quality of life, lost workdays and lost productive time [28]. Depression is an important and frequent condition in primary care, neurology, tertiary and headache clinic settings. It is estimated that depression may be responsible for as much as 25% of all visits to healthcare centers worldwide. In primary care practices, 5-10% of adult patients experience major depression, making it one of the most common disorders seen by primary care physicians. Depression is associated with increased personal suffering, decreased functioning and quality of life. Depression is a common disorder in patients with chronic headache [29-32]. The bidirectional influences and strong interactions between headache and depression have been well-documented, but the exact relationship is not known [21]. Early recognizing and managing depression are a challenging task in chronic headache patients. Chronic Headache patients are time consuming, so often physician misses to screen depression [29]. The Beck Depression Inventory is a validated instrument for the detection and assessment of severity of depression in chronic headache patients [24]. Early screening of depression in chronic headache patients can improve the quality of life [33]. So, physicians should consider having such patients evaluate and if necessary, treat for depression. This study provides the outpatient base data on prevalence of depression among patients with chronic headache in general practice. In this study, high rate of depression was found in patients with chronic headache and it also showed in patients that developed poor quality of life in terms of physical, psychological, social and environmental. Worldwide, the current global prevalence of primary headache is 47%, migraine headache 10%, tension-type headache 38% and chronic daily headache 3%, [21]. Whereas study done at BPKIHS shows prevalence of chronic headache was 1%. In our study, we classified the chronic primary headache according to ICHD3, we found that out of 139 headache patients, 54% were chronic migraine headache patients, 38 % were chronic tension type headache patients and 7.2% were chronic new daily persisting headache, majority were chronic migraine headache as in other studies [34,35]. Yan wang found that 2.7% were CDH patients where they defined CDH according to ICHD [36]. Oshinaike [37] found that Tension-type headache was the most prevalent (72.8%) followed by migraine (18.9%) [37]. This might be due to the population under study. It could also be due to headache diagnostic criteria, the headache diagnosed in this study according to the criteria of the ICHD2. Global studies have actually suggested that approximately 1% of the world’s population may have chronic migraine headache [38,39]. We found that prevalence of chronic migraine headache was high as compared to another headache. [38,39]. There are limited data regarding chronic primary headache on the basis of ICHD3 classification. The mean age of presentation and gender in our study was 35.37 years with a female predominance which is comparable with other studies that reported 20 years to 55 years with mean age 29.57 to 36.9 years [16,34,40]. Multiple studies from the subcontinent have demonstrated that predominantly younger female is prone to have chronic headache. In our study, most of the headache patients were homemaker (64%) followed by skilled worker (20%), student (14.4%), and unskilled worker (0.7%). Most of them were from rural area (55.4%). Study done at BPKIHS found that 51% of headache patients were housewife, 26% were student; 76.8% were Hindu, 8.9% were Buddhist and 10.1 % were Christian, occupation showed statistical significance when compared with subtype of headache [34]. Study done by Manandhar [40] found that there was no association of occupation, TTH was weakly associated with urban dwelling, data regarding rural area people were not given. Most of the headache patients in this study were from rural area, same as described by Manandhar [40]. The prevalence of mild to severe depression in our study was 45.3% which is comparable with other studies that reported 43.6% to 73.8%, [22,36,42,43]. Where mean score of BDI was 12.25. Some studies that used the same psychometric instrument as the one applied in the present work have found an association between depression and chronic headache [30-32]. Other author, Karin Zebenholzer [22] used Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale and found that 43.6% chronic headache patients had depression and he found that depression was more common in chronic headache patients as compared to episodic headache where p < 0.0001 [22]. The study done by Marlow et al and Chung et al found that prevalence rate of mild depression was 63% where prevalence rate was higher than our study, the study based on the Zung Self-Rating scale [41]. This might be due to different psychometric instrument they have used to screened for depression. Our study found that 25.5% had mild depression, 16.5% moderate depression and 2.9% severe depression. Depression was common in CH patients; this could be explained by headache frequency and headache duration. To define chronic headache, pain should be longer than 3 months. Due to longer duration of headache, may affect the patient’s mental health. Chronic illness like diabetes, hypertension has been shown to be associated with depression in many articles [44-46]. So, the Chronicity of headache might be possible confounder and needs to be evaluated further. In our study, 26.61% of chronic migraine headache had (mild to severe) depression, 15.10% chronic tension type headache had (mild to severe) depression and 3.59% chronic new daily persisting headache patients had (mild to severe) depression. Juliane Prieto reported mean BDI score 21 ± 10.7 in chronic migraine patients which was higher (BDI score) as compared to our study (12.89 ±8.3), atleast some degree of depression (mild to severe) appeared in 85.8% of patients.43 More frequency of migraines could directly lead to the presence of depression, which is associated with more depression, shared biological pathways and norepinephrine and serotonin neurotransmitters provide one possible explanation for the co‑occurrence and associations between pain and depressive disorders [21]. Depression was more common in chronic migraine; this could be explained by the severity of headache symptoms; as migraine patients tend to have more severe symptoms. Our study found that depression was common in those patients who were having severe headache as similar study done by Alex [46]. In study done by Alex et al hypothesized that headaches first would be the most common order of onset group, that the headaches first group would have higher headache, and that severity the depression first group would have higher estimated depression. Study done by Nicassio [47] found that the relationship between arthritis pain and depressive symptoms. Other study done by Dohrenwend et al found that chronic myofascial pain developed depression in response to their pain [48]. The findings with arthritis and myofascial pain together suggest a causal relationship between pain and depression. Support from these hypotheses would be consistent with more severe headaches causing depression. Other study by Tae jin Song et al found that anxiety and depression were more common in tension type headache, according to their research 42.2% had tension type headache in which 4.3% suffered from depression where in our study we found depression were common in chronic migraine headache. In our study there was no statistically significant difference between sociodemographic factors with subset of depression as similar to the study done by Tae jin where only gender and occupation showed statistical significance when compared with severity of depression. Our study demonstrated high rates of unemployment among patients with depression, lack of desire and motivation, loss of energy that impaired work function, loss of work productivity. Our study found that depression was more common in female chronic headache patients, womens are more prone to be depressed because of their negative self-evaluation and low self-esteemed they are also influenced by socio-cultural considerations. From our study, we assumed that those with chronic headache are at higher risk for depression than are general population; these findings are particularly salient for the patient with chronic headache. Physicians should be aware about the raised prevalence of depression in patients with chronic headache. Study done by Karin Zebenholdzer [22] showed that depression has a significant impact on quality of life and increase the burden in patients with chronic headache [22]. The study in patients with chronic migraine found that depressive symptoms in these patients were associated with higher disability and lower quality of life, more importantly the quality of life is deceased and the burden is further increased by depression in patients with chronic headache. In our study, we used WHOQOLBREF score to define the quality of life in patients with chronic headache. According to WHOQOLBREF higher the domain score better the quality of life. In our study we compared the mean of two variables (chronic headache with depression and chronic headache without depression with QOL). We found that mean score of Physical QOL (27.38), Psychological QOL (19.99), Social QOL (13.36) and Environmental QOL (31.95) were higher in chronic headache patients with no depression as compared to those with depression. Poor quality of life in CH patients with depression could be explained by patients’ depressive symptoms which were included in BDI scale, that may affect the patient’s mental, physical, psychological, social and environmental quality of life. Study by Maria Palacios et al found an association between headache frequency and duration; more frequent and longer the headache duration, the worse the quality of life [23]. D Amico found that disability and QOL were moderately or little correlated to clinical and psychosocial variables in chronic headache subjects. Chronic migraine with depressive symptoms significantly impacts on disability and QOL [30]. In our study there was no significant association between headache frequency and duration with quality of life. Study done by Subba [49] found that higher levels of depression were found to be associated with reduced quality of life QOL [49] as similar to our study. Where, study done by pompilli has found that comorbid migraine and depression are associated reduced quality of life [50-57]. The Headache is a painful condition related to decreased productivity, limitation of social activities and impaired quality of life [35].
Recommendation: Various studies around the globe identify depression as common co-morbidity among the patients with chronic headache [15]. This study intends to assess the depression among the patients with chronic headache and to describe the quality of life in patients with chronic headache. This article hypothesized that most of the headache patient would have depression with lower scoring of quality of life. This study will provide the outpatient base data on prevalence of depression among patients with primary chronic headache in general practice. To the best of our knowledge, there has not been any study conducted in Nepal. This would help to provide baseline data for further studies. This study would also be helpful to diagnose depression in chronic headache and facilitate early referral to specialists if needed, thereby improving the patient’s quality of life.
Limitations of the study: The BDI is screening tool, used for screening in suspected depression carrier, further work up is needed to diagnose depression. We cannot rule out the possibility of recall bias of the patient reported information. Patient was selected as convenience sampling technique, after being diagnosed as chronic primary headache. This sample may not be totally inclusive of all diagnostic categories. The current study was based exclusively on hospital-based outpatient sample therefore, may not be the representative sample of patients in the community.
CONCLUSION
The Headache is an excruciating ailment related to decreased efficiency, limitation of social activities and impaired quality of life. In this study rural middle age female with family history of chronic headache have moderate depression. The QOL decrease as increase in BDI score.
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :