-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Muhammad Aqil Kamaruddin, May Khin Soe*, Muhammad Alif Najman Mazlan, Wan Muhammad Irfan Wan Rishdi and Pan Thu Ta
Corresponding Author: May Khin Soe, Assistant Professor, Department of Basic Medical Sciences, Kulliyyah of Pharmacy, International Islamic University Malaysia, Jalan Sultan Ahmad Shah, 25200 Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia.
Received: March 20, 2025 ; Revised: March 26, 2025 ; Accepted: March 29, 2025 ; Available Online: April 09, 2025
Citation: Kamaruddin MA, Soe MK, Mazlan MAN, Rishdi WMNW & Ta PT. (2025) A Systematic Review: An Analysis of the Promising Effects of Myo-inositol and Probiotics on the Prevention of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J Pharm Sci Drug Discov, 4(1): 1-13.
Copyrights: ©2025 Kamaruddin MA, Soe MK, Mazlan MAN, Rishdi WMNW & Ta PT. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) poses significant health risks for both mothers and infants, and this prevalence of the condition has significantly grown globally, necessitating effective preventive strategies. Myo-inositol and probiotics seem to have potential effects as supplements for GDM prevention.
Materials and method: This systematic review adhered to the PRISMA guidelines. A comprehensive literature search was performed in PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, Science Direct, and Snow ball technique was used to enhance the thoroughness of literature search. The retrieved papers were screened separately by two reviewers according to the eligibility criteria, in phases including title, abstract, and full text. The potential for bias in the included papers was evaluated separately by using the critical evaluation checklist from the Joanna Briggs Institute. Data from the included studies were extracted and presented in the table to analysis by the authors.
Results: Out of the 311 articles, 11 articles fulfilled our eligibility criterion. Based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, four studies involving myo-inositol reported a significant reduction of GDM occurrence while no studies involving probiotics reported a significant effect of it on GDM prevention. No notable advantages or disadvantages were observed concerning the secondary outcomes, such as complications for both the infant and mother associated with GDM when using myo- inositol and probiotics supplements.
Conclusion: A combination of 4 gms of MI and 400 mg of folic acid (FA) has better beneficial nutrient for preventing GDM when started at around 12-13 weeks of pregnancy and continued until delivery. Although probiotics did not demonstrate preventative benefits on gestational diabetes mellitus GDM, they may have potential impacts on glucose metabolism in pregnant women when lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium subspecies strains are administered starting at 12-13 weeks of gestation.
Keywords: Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), Myo-inositol, Probiotics, Prevention, Supplementation
INTRODUCTION
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that are first detected during gestation. GDM is the most prevalent medical problem during pregnancy [1]. The prevalence of the condition has significantly grown. The latest meta-analysis reported that the worldwide prevalence of GDM was found to be 14.7%. This estimation has been determined on the guidelines established by the International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG), which is the most often employed diagnostic approach globally [2]. A previous study conducted in Malaysia based in Selangor reported that the prevalence of GDM was 27.9%, which is significantly higher compared to other studies [3].
There are a few diagnostic methods that can be used to diagnose GDM which are 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) or 100-g OGTT. Women with a heightened susceptibility for having GDM require screening using 75-g OGTT. If the test yields a negative result, the procedure should be redone during the 24th to 28th week of gestation. Meanwhile, for women who are 25 years old and above and do not have any additional risk factors, the screening is often conducted between the 24th and 28th weeks of gestation. GDM is diagnosed when any one of these outcomes is present: the criteria for diagnosing diabetes include a fasting plasma glucose (FPG) level of 5.1mmol/L or higher, or a 2-h post- glucose challenge level of 7.8mmol/L or more [4].
The onset of GDM is influenced by several variables, including an intricate interaction of genetic, metabolic, and external factors. During pregnancy, there is an increase in insulin production that coincides with the development of insulin resistance. However, individuals with GDM experience a deficiency in the capacity of β-cells to sufficiently counteract insulin resistance. As a result, they are unable to sustain normal levels of blood glucose. GDM arises from an inability to tolerate carbohydrates as a result of anomalies in three key elements of fuel metabolism: impaired insulin sensitivity, diminished insulin secretion, and heightened hepatic glucose production [5].
GDM has both immediate and long-lasting effects on both mothers and fetuses. Mothers diagnosed with GDM may encounter delivery challenges in the immediate term, such as the need for induced labor or caesarean section, primarily due to the baby's size or other related concerns [6]. In addition, they may also suffer from hypertension and have an elevated probability of needing caesarean births because of problems. Moreover, maternal who had GDM have an increased probability of having Type 2 diabetes in the future. Additionally, they are more susceptible to cardiovascular problems [7,8]. Short-term effects on the fetus include increased birth weight (macrosomia), elevated risk of hypoglycemia at delivery, and a little heightened susceptibility to respiratory issues [9].
Recently, emerging research indicated that the use of probiotics and myo-inositol (MI) holds potential in avoiding GDM, although definitive conclusions were still being established.
Inositol are polyols with a six-carbon ring structure that have all their carbon atoms hydroxylated. Many of these sugar-alcohol isomers have biological activity; the most prevalent is MI [10]. According to studies, MI may improve insulin sensitivity across a range of tissues, which might lead to better absorption and use of glucose. It may contribute to improved glycemic control by modifying insulin signaling pathways, especially by affecting the uptake and metabolism of glucose in cells [11]. Additionally, in conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), MI has shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity and menstrual regularity [12]. Probiotics are microorganisms that are living and active. By altering the host's immune system or gut flora and/or affecting it, they can promote health when given at therapeutic doses [13]. Certain probiotic strains have been related to increased insulin sensitivity, which may help to better control blood sugar levels by enabling the body to use glucose more effectively. Probiotics can also alter the makeup and activity of the gut microbiota, which may have a beneficial effect on metabolic health. Certain strains could have anti-inflammatory qualities, which could lower inflammation indicators connected to insulin resistance [14]. In addition, probiotics generate metabolic byproducts and short-chain fatty acids that may contribute to improving insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism [15]. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the potential effects of MI and probiotics as GDM prevention by systemically review available published articles and research.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eligibility Criteria
This systematic review analyzed the effectiveness of MI and probiotics as supplementations for GDM prevention. To assure the relevance of the selected studies to the research issue, criteria for study inclusion were defined.
Inclusion criteria
The relevance studies will be selected if they were published within the last 10 years (2013-2023).
To be considered for inclusion within this review, the subjects selected must be pregnant women without comorbidities and pre-pregnancy normal glucose level.
Studies focused on MI and probiotics as interventions during pregnancy for GDM prevention were included.
Only studies with full text availability and English language were included. As this review analyzed the effect of MI and probiotics as GDM prevention the studies selected must reported the data on GDM occurrence and plasma glucose level (primary outcome). The subjects were screened for GDM occurrence using 75-g OGTT.
This review included the papers that examined the association between GDM and both mother and newborn problems, such as macrosomia, caesarean delivery, preterm delivery, and preeclampsia (included as secondary outcomes).
Exclusion criteria
Studies were excluded if interventions other than probiotics and MI were used and pre- diabetes pregnant women or existence GDM and with other comorbidities as subjects.
This study published before 2013, studies with inadequate data, non-human subject, and animal studies, other than English language, review articles and study protocols were excluded.
Search Strategy
Studies or papers were retrieved from four databases, namely SCOPUS, Cochrane Library, PubMed, and Science Direct. The search approach included a blend of domain and sub-domain, joined with Boolean operators "OR" and "AND". Keywords within the same domain were linked using the Boolean operator "OR" whereas the operator "AND" was used to link keywords between other domains. The keywords used in this review were gestational diabetes mellitus, prevention, probiotics, and MI. The keywords and their synonyms are summarized in Table 1. Grey literature and references of relevant articles were also used to show broader evidence in diverse types of studies.
Table 1. The keywords used in search of articles from databases.
|
Domain |
Subdomain |
|
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus |
“Gestational Diabetes Mellitus” OR “Gestational Diabetes” OR GDM OR “Pregnancy-induced diabetes” OR “Diabetes during pregnancy” |
|
Prevention |
“Prevention” OR “Preventive measures” OR “Interventions to prevent” OR Prophylaxis |
|
Probiotics |
Probiotics OR “Microbial supplements” |
|
Myo-Inositol |
Myoinositol OR “myo-inositol” OR Inositol OR Inositol OR “vitamin B8” |
Study selection
Two authors thoroughly and autonomously evaluated the search results according to predetermined eligibility criteria during the stages of title, abstract, and full-text research selection. The screening authors had full access to the details of the studies and were not blinded. Two different authors conducted a separate evaluation of study titles and abstracts until they reached a point of agreement. The writers engaged in discussions to address any disparities. If an agreement could not be reached, the third author was included to further explore the discrepancies and reach the decision. Studies that met the specified criteria were obtained for a thorough evaluation of the complete text. The full-text screening was conducted through a process of independent double screening by the two writers. Problems that arose at this stage were handled by deliberation and consensus between the two writers. If the authors failed to reach an agreement, the problems were then addressed with the involvement of the third author. The authors were contacted, if necessary, to obtain further clarification on any missing or insufficient information to establish the eligibility of the study. The main rationale for the removal of papers was thoroughly recorded at every level of the research selection process. The research selection was performed via Microsoft Excel. A definitive compilation of papers was compiled and kept in Mendeley and Microsoft Excel for the purpose of extracting data.
Data collection/extraction
The studies that met the criteria were assessed by the author, and the data that were important were extracted. The extracted data encompassed details such as authors, publication year, study region, study design, total number of participants recruited, study intervention, duration of intervention, and the findings or results of primary and secondary outcomes. The data from each research were inputted into a table in Microsoft Excel to facilitate the analysis of the included studies. The numerical data were extracted and presented as the mean ± standard deviation, or mean (SEM), along with p-values. Statistical significance was determined when p < 0.05.
Risk of bias in individual studies
Two reviewers independently assessed the risk of bias in each of the articles included by evaluating their methodological quality using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical assessment checklists [16]. A score of '1' was assigned if the studies met the specified requirements of the checklist, and '0' if they did not. Subsequently, the cumulative score was computed and subsequently transformed into a percentage. Research studies with a percentage below 50% were categorized as having a high risk of bias. Studies with a percentage between 50% and 69% were regarded to have a moderate risk of bias, while studies with a percentage of 70% or more were classified as having a high risk of bias [17]. Any disputes will be settled through dialogue between the two writers and subsequently with the third author if consensus was not reached between the two authors. The risk of bias for each kind of included research was visualized using traffic-light plots generated by the Risk-of-bias visualization (robvis) tool [18].
RESULTS
Study Selection
A comprehensive search yielded a total of 386 studies across four databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Science Direct. Three studies were found using snowball technique by going through the references in the related articles. PubMed recorded 37 studies, Scopus recorded 57 studies, Cochrane recorded 116 studies and Science Direct recorded 173 studies. From the total searching result, we excluded 72 studies as they were duplicated in the databases used. A total of 311 studies were screen by reviewing the title and abstract. 296 studies were excluded as they were review articles (n=12), study protocol (n=21), wrong study population (n=16) and unrelated studies (n=247). After reviewing the title and abstract, 15 studies were remained, and full-text screening were conducted. For the studies that we found using snowball technique, we recorded three studies, however one studies cannot be retrieved as its full text was inaccessible, leaving two studies. At the end of the study selection process (Figure 1), we concluded that 11 studies were eligible to be included in this systematic review.
Study Characteristics
The studies selected in this systematic review were published between year 2013 to 2023. All the studies were randomized controlled trial which were conducted in Italy (n=4), Ireland (n=2), Iran (n=2), Australia (n=1), New Zealand (n=1), and Finland (n=1). Five studies selected used MI as their intervention while six studies used probiotics as their intervention. Two studies recruited pregnant women with family history of diabetes [19,20] two studies with obese pre-pregnancy [21,22] two studies with overweight pregnant women [23,24] three studies that included both obese and overweight pregnant women [25-27] one studies with high risk pregnant women [28] and one studies recruited pregnant women with a personal or partner history of atopic disease [29]. All the studies used 75-g 2-h OGTT as the GDM screening tool except for one study by Lindsay et al. (2014) [22] that used 100-g 3-h OGTT. For studies that used MI as their intervention, four studies used 4g MI + 400 mg FA [19,21,23,24] and one studies used combination of MI 1,100mg plus di-chiro inositol (DCI) 27.6mg+ 400 mg FA [20]. For studies that used probiotics as their intervention, two studies used Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LGG) plus Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis [26,27], one study used Lactobacillus acidophilus plus Bifidobacterium Lactis [25], one study used Lactobacillus rhamnosus alone [29], one study used Lactobacillus salivarius alone [22] and one study used combinations of Lactobacillus acidophilus plus Bifidobacterium longum plus Bifidobacterium bifidum [28]. The details of the basic characteristics of included studies were summarized in Table 2.
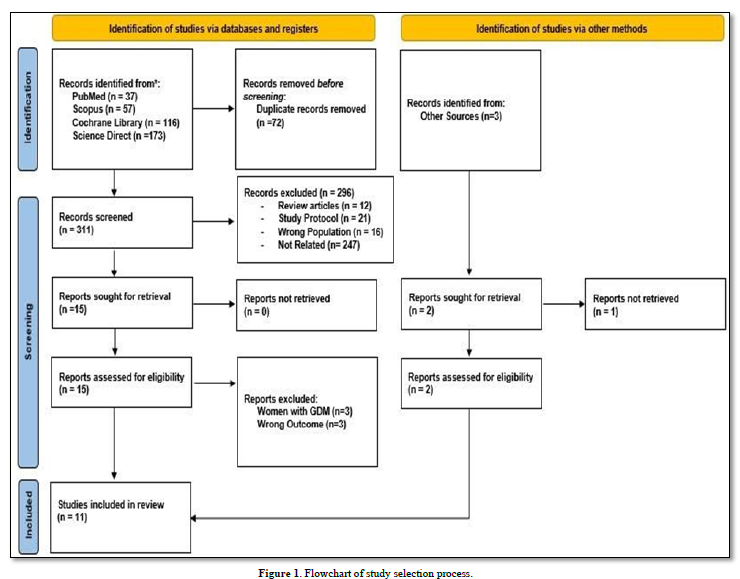
Table 2. Basic characteristics of included studies of myo-inositol.
|
Author (Year) |
Study Design |
Country Diagnosis of GDM |
Sample size (I/C) |
Population Inclusion Characteristic |
Age (I/C) |
BMI (kg/m2) (I/C) |
Intervention (I/C) |
Duration of Intervention |
Outcomes |
GDM Occurrence (I/C) |
|
Myo-inositol Studies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D’Anna (2013) [19] |
Randomized, open-label, placebo-controlled study |
Italy, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
99/98 |
Family History of Type-2 DM |
31.0/31.6 |
22.8/23.6 |
I: 4g MI + 400 mg FA C: 400 mg FA |
12-13th weeks of gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↓ - Macrosomia↓ - Caesarean section↔ - Preterm delivery↔ - Neonatal hypoglycemia↔ - Distress respiratory syndrome ↔ - Shoulder dystocia↔ - Weight gain at OGTT ↔ Gestational hypertension↔ |
6/15 (P=0.04) |
|
D’Anna (2015) [21] |
Randomized, open-label, placebo-controlled study |
Italy, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
97/104 |
Obese Pre-pregnancy (BMI ≥ 30) |
30.9/31.7 |
33.8/33.8 |
I: 4g MI + 400 mg FA C: 400 mg FA |
12-13th weeks of Gestation until delivery |
- GDM↓ - Macrosomia ↔ - Caesarean delivery↔ - Gestational hypertension ↓ - Insulin treatment ↔ - Neonatal hypoglycemia ↔ - Preterm delivery ↔ - Shoulder dystocia ↔ - Transferred to NICU ↓ - Weight gain at OGTT ↑ |
14%/33.6% (P=0.001) |
|
Santamaria (2016) [23] |
Randomized, open-label, placebo-controlled study |
Italy, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
95/102 |
Overweight women |
32.1/32.7 |
26.9/27.1 |
I: 4g MI + 400 mg FA C: 400 mg FA |
12-13th weeks of gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↓ - Weight gain at OGTT ↔ - Caesarean section ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Preterm delivery ↔ - Gestational hypertension ↔ - Transferred to NICU ↔ - Shoulder dystocia ↔ - Insulin treatment ↔ - Neonatal hypoglycemia ↔ |
11.6%/27.4% (P=0.004) |
|
Farren (2017) [20] |
Randomized, open-label, placebo-controlled study |
Ireland, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
120/120 |
Family History of Type-1/2 DM |
31.1/31.7 |
26.0/26.2 |
I: MI 1,100mg+Dichiro Inositol 27.6mg+ 400 mg FA C: 400 mg FA |
10-16th weeks of gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Caesarean delivery ↔ - Gestational hypertension ↔ - Preterm delivery ↔ - Shoulder dystocia ↔ - NICU admissions ↔ - Hypoglycemia ↑ - Neonatal jaundice ↓ - Respiratory distress ↔ |
23%/18% (P=0.34) |
|
Vitale (2021) [24] |
Randomized, open-label, placebo-controlled study |
Italy, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
110/113 |
Overweight Women (BMI ≥25 and ≤ 30) |
27.2/23.0 |
27.0/26.7 |
I: 4g MI + 400 mg FA C: 400 mg FA |
12-13th weeks of gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↓ - Weight gain at OGTT ↓ |
8.2%/21.2% (P=0.006) |
|
Probiotic Studies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- |
|
|
Lindsay (2014) [22] |
Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial |
Ireland, 100-g 3h OGTT |
63/75 |
Obese Women (BMI: 30.0-39.9) |
31.4/31.0 |
32.9/34.1 |
I: 100 mg Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118 (109 CFU) C: not stated the content |
24-28th weeks of gestation |
- GDM ↔ - Preeclampsia ↔ - Gestational hypertension ↔ - Caesarean ↔ - Excess weight gain ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Admission to NICU ↔ |
16.1%/14.9% (P=0.561) |
|
Wickens (2017) [29] |
Double- blind, randomized, placebo-controlled parallel trial |
New Zealand, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
184/189 |
Pregnant women with a personal or partner history of atopic disease |
34/34 |
25.0/26.0 |
I: Lactobacillus rhamnosus (6 ×109 CFU) C: maize- derived maltodextrin |
14-16th weeks of gestation until 6 months postpartum |
- GDM ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Premature ↔ - Admission to NICU ↔ |
8.2%/13.8% (P=0.12) |
|
Callaway (2019) [26] |
Double-blind randomized controlled trial |
Australia, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
204/207 |
Obese and Overweight Women (BMI≥25) |
31.7/31.3 |
31.6/31.9 |
I: Lactobacillus rhamnosus (LGG) and Bifidobacterium animalis subspecies lactis (BB-12) (>1X109 CFU/day) C: microcrystalline cellulose and dextrose anhydrate capsules |
Prior 20th weeks of Gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↔ - Preeclampsia ↔ - Gestational hypertension ↔ - Caesarean ↔ - Preterm ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Admission to NICU ↔ - Neonatal Hypoglycemia ↔ |
12.3%/18.4% (P= 0.10) |
|
Pellonperä (2019) [27] |
Double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial |
Finland, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
99/91 |
Obese and Overweight Women (BMI≥25) |
30.8/30.4 |
29.9/29.7 |
I: Lactobacillus rhamnosus + Bifidobacterium animalis ssp. Lactis (1010 CFU) C: microcrystalline cellulose |
14th weeks of gestation until 6 months postpartum |
- GDM ↔ - Caesarean ↔ - Preeclampsia ↔ - Gestational hypertension ↔ - Weight gain at OGTT ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Premature ↔ - Admission to NICU ↔ - Neonatal Hypoglycemia ↔ |
35.4/39.6 (P=0.87) |
|
Asgharian (2020) [25] |
Triple-blind, randomized placebo-controlled two-parallel trial |
Iran, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
64/64 |
Obese and Overweight Women (BMI ≥ 25) |
29.5/29.4 |
29.2/30.3 |
I: 100 g yogurt with additional Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium Lactis (5x108 CFU/g) C: Conventional Yogurt |
24th weeks of gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↔ - Preeclampsia ↔ - Caesarean delivery - Weight gain over pregnancy ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ - Admission to NICU ↔ |
9%/17% (P=0.184) |
|
Shahriari (2021) [28] |
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial |
Iran, 75-g 2-h OGTT |
241/266 |
High risk women |
31.8/32.3 |
30.3/30.2 |
I: 500 mg probiotic capsule was a mixture of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA1 (> 7.5 × 109 CFU) +Bifidobacteriu m longum (> 1.5 × 109 CFU) + Bifidobacterium bifidum sp9 cs (> 6 × 109 CFU) C: 500 mg starch and maltodextrins |
14-24th weeks of gestation until delivery |
- GDM ↔ - Caesarean ↔ - Preeclampsia ↔ - Macrosomia ↔ |
41.9%/40.2% (P=0.780) |
I/C: Intervention/control; BMI: Body mass index; NICU: Neonatal intensive care unit
Risk of bias of individual studies
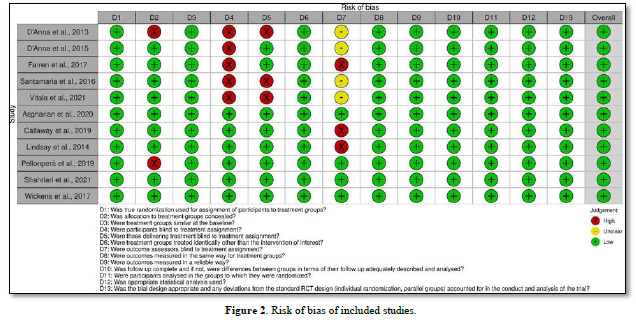
All of eleven selected RCTs papers demonstrated overall insignificant risk of bias using JBI risk of bias tools. For domain one, three, six, eight until 13, all studies demonstrated insignificant risk of bias. For domain two, two studies recorded high risk of bias as the allocation of the treatment were not concealed. For domain four, five studies demonstrated high risk of bias as the participants were not blind to treatment assignment due to they were open label study. For domain five, three studies had high risk of bias as those that delivered the treatment were not blinded to the treatment assignment. For domain seven, three studies had high risk of bias as the outcome assessors were not blinded to the treatment assignment and it was unclear for four studies. Figure 2 summarized the result of the risk of bias of included studies.
Individual outcomes of the studies
In this systematic review, the targeted primary outcomes were GDM occurrence and blood glucose levels at OGTT (FPG, 1-h post-load and 2-h post-load). The targeted secondary outcomes that were analyzed in this study were maternal and neonatal outcomes (macrosomia, preterm birth, caesarean section, preeclampsia, and others). All included studies reported the primary outcomes except for Lindsay [22], that did not report on 1-h and 2-h glucose at OGTT.
Four out of five studies on MI [19,21,23,24] reported GDM prevalence reduced significantly in the intervention groups (P<0.05) and one studies reported it was increased in the intervention group but did not differ significantly. For FPG at OGTT and 1-h glucose OGTT, two out of five studies of MI studies [19,21] showed significant reduction (P<0.05), while the others two studies did not differ significantly. For 2-h glucose at OGTT, there were no significant difference effect of MI for these five studies [19-21,23,24].
For study that reported on probiotics as intervention, three studies showed a reduction in GDM prevalence [25,27,29] and three studies showed an increased in GDM prevalence [26,22,28] but all of them were not differ significantly. For FPG at OGTT, Asgharian [25] reported significant reduction while Callaway et al., (2019) [26] reported significant increment. The other four studies reported the effect of probiotics did not differ significantly on FPG at OGTT [22,27-29]. For 1-h and 2-h glucose at OGTT, all five studies showed no significant effect on them [25-28]. Data were summarized in Table 3.
Table 3. Primary outcomes of included studies.
|
Myo-inositol studies |
|
Probiotics studies |
|
|
Author (Year) |
Targeted Primary Outcomes |
Author (Year) |
Targeted Primary Outcomes |
|
D’Anna (2013) [19] |
GDM Prevalence: Significantly lowered in the treatment group compared to control, 6 cases versus 15 cases, (P=0.04). |
Asgharian (2020) [25] |
GDM Prevalence: Reduced in the treatment group versus placebo, 9% (n=6) versus 17% (n=11) but did not differ significantly, (P=0.04). |
|
FPG at OGTT: Significantly lowered in the treatment group, 77.0 ± 6.7mg/dL, compared to placebo, 80.5 ± 8.1 mg/dL, (P=0.001). |
FPG at OGTT: Significantly reduced in the intervention group, 74.8 ± 7.4 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 77.9 ± 11.2 mg/dL, (P=0.008). |
||
|
1-h glucose OGTT: Significantly lowered in the treatment group, 123.0 ± 30.6 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 133.0 ± 30.5 mg/dL, (P=0.02). |
1-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 128.0 ± 28.4 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 136.0 ± 31.7 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.071). |
||
|
2-h glucose OGTT: No significant reduction in both groups, 105.6 ± 22.0 mg/dL versus 110.1 ± 26.5 mg/dL. (P=0.2). |
2-h glucose OGTT: Significantly reduced in the intervention group, 103.9 ± 21.0 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 115.5 ± 26.3 mg/dL, (P=0.002). |
||
|
D’Anna (2015) [21] |
GDM Prevalence: Significantly lowered in the treatment group compared to control, 14% versus 36%, (P=0.001). |
Callaway (2019) [26] |
GDM Prevalence: Increased in the treatment group versus placebo, 18.4% (n=38) versus 12.3% (n=25), but did not differ significantly, (P=0.10). |
|
FPG at OGTT: Significantly lowered in the treatment group, 80.6 ± 7.3 mg/dL, compared to placebo 84.6 ± 10.4 mg/dL, (P=0.001). |
FPG at OGTT: Significantly increased in the intervention group, 79.3 ± 9.0 mg/dL, compared to control, 77.5 ± 8.1 mg/dL, (P=0.049). |
||
|
1-h glucose OGTT: Significantly lowered in the treatment group, 128.5 ± 34.1 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 143.1 ± 31.3 mg/dL, (P=0.002). |
1-h glucose OGTT: Increased in the intervention group, 128.0 ± 28.4 mg/dL, compared to control, 136.9 ± 32.4 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.75). |
||
|
2-h glucose OGTT: Significantly lowered in both groups, 105.1 ± 25.2 mg/dL versus 122.9 ± 30.2 mg/dL for intervention and control group respectively, (P <0.001). |
2-h glucose OGTT: Increased in the intervention group, 115.3 ± 27.0 mg/dL, compared to control, 113.5 ± 25.2 mg/dL, (P=0.37). |
||
|
Farren (2017) [20] |
GDM Prevalence: No significant difference between groups with 28 cases (23%) and 22 cases (18%) for intervention and control group respectively (P=0.34). |
Lindsay (2014) [22] |
GDM Prevalence: Increased in the treatment group, 16.1% (n=10) versus placebo 14.9% (n=11), but did not differ significantly, (P=0.561). |
|
FPG at OGTT: Not differ significantly between groups with 81.0 ± 14.3 mg/dL versus 81.0 ± 10.9 mg/dL for intervention and control group respectively, (P=1.00). |
FPG at OGTT: Decreased in the intervention group, 4.60 ± 0.4 mmol/L, compared to control 4.69 ± 0.46 mmol/L, (P=0.391). |
||
|
1-h glucose OGTT: Not differ significantly in the intervention group, 138.4 ± 49.9 mg/dL compared to placebo 133.2 ± 35.0 mg/dL, (P=0.42). |
1-h glucose OGTT: Not reported. |
||
|
2-h glucose OGTT: No significant reduction in both groups, 102.6 ± 30.2 mg/dL versus 97.2 ± 24.8 mg/dL for intervention and control group respectively, (P=0.07). |
2-h glucose OGTT: Not Reported. |
||
|
Santamaria (2016) [23] |
GDM Prevalence: Significantly reduced in the intervention group compared to control, 11.6 % (n=11) versus 27.4 % (n=28), (P=0.004). |
Pellonperä (2019) [27] |
GDM Prevalence: Decreased in the treatment group, 35.4% (n=35) versus control, 39.6% (n=36), but did not differ significantly, (P=0.87). |
|
FPG at OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 80.5 ± 7.3 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 82.5 ± 8.6 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.09). |
FPG at OGTT: Increased in the intervention group, 4.9 ± 0.43 mmol/L, compared to control, 4.8 ± 0.32 mmol/L, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.11). |
||
|
1-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 128.5 ± 30.2 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 133.4 ± 32.2 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.3). |
1-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 7.5 ± 1.7 mmol/L compared to control, 7.7 ± 1.6 mmol/L, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.44). |
||
|
2-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 106.6 ± 28.0 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 113.4 ± 27.4 mg/dL but did not differ significantly, (P=0.07). |
2-h glucose OGTT: Increased in the intervention group, 6.5 ± 1.3 mmol/L compared to control 6.4 ± 1.4 mmol/L, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.87). |
||
|
Vitale (2021) [24] |
GDM Prevalence: Significantly lowered in the treatment group compared to control, 8.2 % (n=9) versus 21.2 % (n=24), (P=0.006). |
Shahriari (2021) [28] |
GDM Prevalence: Increased in the intervention group, 41.9% compared to control 40.2%, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.780). |
|
FPG at OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 84.13 ± 12.94mg/dL, compared to placebo, 86.61 ± 23.89 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.3374). |
FPG at OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group 88.68 mg/dL compared to control 89.61 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.338). |
||
|
1-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 144.09 ± 21.10 mg/dL, compared to placebo,148.01 ± 27.42 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.2338). |
1-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 163.86 mg/dL compared to control 166.88 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.116). |
||
|
2-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 115.08 ± 19.21 mg/dL, compared to placebo, 120.71 ± 25.8 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.0666). |
2-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group 138.39 mg/dL compared to control 139.27 mg/dL, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.599). |
||
|
|
|
Wickens (2017) [29] |
GDM Prevalence: Decreased in the treatment group, 8.2% (n=15) versus placebo, 13.8% (n=26), but did not differ significantly, (P=0.12). |
|
FPG at OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 4.32 mmol/L compared to control, 4.40 mmol/L, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.06). |
|||
|
1-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 6.71 mmol/L compared to control 6.89 mmol/L, but did not differ significantly, (P=0.42). |
|||
|
2-h glucose OGTT: Reduced in the intervention group, 5.65 mmol/L compared to control 5.78 mmol/L, but did not differ significantly (P=0.39). |
Secondary outcomes that were related to maternal and neonatal consequences also reported in the included studies. For maternal outcomes, nine out of 11 studies reported on caesarean section cases, five studies reported on preeclampsia; seven studies reported on gestational hypertension, seven studies reported on gestational weight gain, two studies reported on insulin treatment. For neonatal outcomes, only one studies did not report on macrosomia, seven studies reported on preterm delivery, four studies reported on shoulder dystocia, eight studies reported on NICU admission, five studies reported on neonatal hypoglycemia, and two studies reported on distress respiratory syndrome. The result of the secondary outcomes of individual studies were tabulated in Table 4.
Table 4. Secondary outcomes of included studies.
|
Myo-inositol Studies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
D’Anna (2013) [19] |
D’Anna (2015) [21] |
Santamaria (2016) [23] |
Farren (2017) [20] |
Vitale (2021) [24] |
|
Secondary Outcomes |
Intervention/ Placebo |
|
|
|
|
|
Maternal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Caesarean Section |
42.4% / 43.8% ↔ |
42 (43.3) / 48 (46.1) ↔ (P=0.68) |
38 (40) / 49 (48) ↔ (P=0.3) |
37 (32) / 41 (35) ↔ (P=0.58) |
NA |
|
Preeclampsia |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
Gestational hypertension |
3 cases /2 cases ↔ |
0 / 6 (5.8) ↓ (P=0.02) |
1 (1) / 4 (3.9) ↔ (P=0.2) |
2 (2) / 8 (7) ↔ (P=0.11) |
NA |
|
Weight gain at OGTT (kg) |
7.2 ± 2.6 / 7.0 ± 3.9 ↔ (P=0.29) |
5.9 ± 4.7 / 4.6 ± 4.5 ↑ (P=0.04) |
6.2 ± 3.2 / 7.5± 4.0 ↔ (P=0.07) |
NA |
8.33 ± 2.47 / 9.31 ± 2.66 ↓ (P=0.0070) |
|
Insulin treatment |
NA |
2 (2.1) / 4 (3.8) ↔ (P=0.72) |
2 (18.2) / 4 (14.3) ↔ (P=0.85) |
NA |
NA |
|
Neonatal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Macrosomia |
0 / 7 ↓ (P=0.007) |
5 (5.1) / 5 (4.8) ↔ (P=0.89) |
1 (1) / 5 (4.9) ↔ (P=0.2) |
14 (12) / 9 (8) ↔ (P=0.27) |
NA |
|
Preterm delivery |
3 / 4 ↔ |
3 (3.1) / 10 (9.6) ↔ (P=0.06) |
2 (2.1) / 8 (7.8) ↔ (P=0.3) |
2 (2) / 8 (7) ↔ (P=0.11) |
NA |
|
Shoulder dystocia |
1 / 2 ↔ |
1 (1.0) / 1 (0.9) ↔ (P=0.96) |
0 / 1 (1) ↔ (P=0.9) |
0 / 0 |
NA |
|
Transferred to NICU |
NA |
0 / 5 (4.8) ↓ (P=0.03) |
1 / 1(1) ↔ (P=0.9) |
4 (3) / 6 (5) ↔ (P=0.51) |
NA |
|
Neonatal hypoglycemia |
0 / 0 |
0 / 1 (0.9) ↔ (P=0.88) |
0 / 1 (3.6) ↔ (P=0.62) |
9 (8) / 1 (1) ↑ (P=0.01) |
NA |
|
Distress respiratory syndrome |
1 / 1 ↔ |
NA |
NA |
2 (2) / 1 (1) ↔ (P=0.56) |
NA |
|
Probiotic Studies |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lindsay (2014) [22] |
Wickens (2017) [29] |
Pellonperä (2019) [27] |
Callaway (2019) [26] |
Asgharian (2020) [25] |
Shahriari (2021) [28] |
|
Secondary Outcomes |
Intervention/ Placebo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maternal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Caesarean Section Case |
20 (32.8) / 25 (34.7) ↔ (P=0.744) |
NA |
4 (4.2) / 6 (6.5) ↔ (P=0.28) |
73 (35.3) / 80 (39.2) ↔ (P=0.41) |
33 (52) / 35 (55) ↔ (P=0.695) |
135 (56.0) / 156 (58.6) ↔ (P=0.550) |
|
Preeclampsia |
3 (4.8) / 2 (2.7) ↔ (P=0.366) |
NA |
4 (4.2) / 2 (2.2) ↔ (P=0.80) |
19 (9.2) / 10 (4.9) ↔ (P=0.09) |
1 (2) / 0 ↔ (P=0.997) |
43 (17.8) / 46 (17.3) ↔ (P=0.870) |
|
Gestational hypertension |
5 (7.9) / 3 (4.0) ↔ (P=0.289) |
NA |
4 (4.2) / 4 (4.3) ↔ (P=0.80) |
10 (4.9) / 11 (5.4) ↔ (P=0.74) |
NA |
NA |
|
Weight gain at OGTT (kg) |
11.1 ± 6.2 / 9.4 ± 5.6 ↔ (P=0.479) |
NA |
21.6 / 21.3 ↔ (P=0.51) |
NA |
9.37 (2.8) / 9.34 (3.4) ↔ (P=0.976) |
NA |
|
Insulin treatment |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
Neonatal |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Macrosomia |
6 (9.8) / 7 (9.7) ↔ (P=0.844) |
46 (22.4) / 32 (15.8) ↔ (P=0.10) |
13 (13.5) / 13 (14.1) ↔ (P=0.26) |
31 (15.0) / 35 (17.2) ↔ (P=0.56) |
3 (5) / 3 (5) ↔ (P=0.999) |
13 (5.4) / 9 (3.4) ↔ (P=0.260) |
|
Preterm delivery |
NA |
16 (7.8) / 8 (4.0) ↔ (P=0.10) |
4 (4.2) / 3 (3.3) ↔ (P=0.05) |
17 (8.8) / 12 (6.7) ↔ (P=0.43) |
NA |
NA |
|
Shoulder dystocia |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
|
Transferred to NICU |
9 (14.8) / 9 (12.3) ↔ (P=0.691) |
23 (11.3) / 22 (11.0) ↔ (P=0.90) |
13 (13.5) / 11 (12.0) ↔ (P=0.76) |
42 (20.3) / 43 (21.6) ↔ (P=0.75) |
2 (3) / 2 (3) ↔ (P=0.980) |
NA |
|
Neonatal hypoglycemia |
NA |
NA |
20 (21.1) / 12 (13.5) ↔ (P=0.48) |
25 (12.4) / 27 (13.5) ↔ (P=0.73) |
NA |
NA |
Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation or number (percent of within group)
DISCUSSION
Preventing GDM is of utmost importance, since it directly impacts the health and well-being of both the mother and the newborn. It is because GDM is recognized as a contributing factor towards the development of parental and perinatal problems [30]. Hence, in this study, our objective is to examine the impact of MI and probiotics on the development of GDM, as well as the results for both the mother and the newborn.
Based on our results, we found that MI able to reduce GDM prevalence when the participants undergone OGTT at 24-28 weeks. Four studies reported MI significantly reduced GDM occurrence (P<0.05) in type 1 and 2 DM family history, obese and overweight women and high-risk pregnant women shown in Table 2. Each of these four trials utilized a combination of 2g of MI and 200 mg of FA, which was administered to the participants daily at 12-13 weeks of gestation until delivery. The first semester is very crucial for fetal development. The placenta is fully developed and functioning by 12th-13th week of pregnancy. Thus, the supplementation can support both mother and fetal health and optimally prevent the GDM. On the other hand, research that was carried out by Farren [20] used the combination of 1.1 g of MI, 27.6 mg of di-chiro inositol (DCI), and 400 mg of FA, and it demonstrated that there was no significant influence on the development of GDM. In comparison to prior studies that utilized 4 gms of MI, this demonstrated that the combination of MI and DCI at a lower dose, which was 1.1 gms of MI, would not have a favorable impact as GDM preventive supplements. Four studies also demonstrated that MI may reduce the FPG, 1-h and 2-h post load at OGTT, thus giving the patient beneficial effect on their glucose metabolism (Table 3). Other systematic reviews also shown the same result of MI in preventing GDM [31-33]. Thus, MI is considered an effective and safe to reduce the risk of GDM by improving insulin sensitivity, regulating the blood glucose level during pregnancy and reducing the pregnancy outcome and complications.
For maternal outcomes, five studies reported the reduction of caesarean section cases in the intervention group, but the data were not statistically significant. For gestational hypertension, two studies showed a reduction of the cases and one study reported 3 cases in the intervention group compared 2 cases in placebo but they were not statistically significant (Table 3) on the other hand D’Anna [21] reported a significant reduction of gestational hypertension in intervention group (P=0.02). For weight gain at OGTT, two studies reported contradict outcome as D’Anna [21] reported significant increment while Vitale [24] reported significant reduction. This might be due to the different population recruitment in both studies as D’Anna [21] recruited obese pregnant women while Vitale [24] recruited overweight pregnant women. Thus, MI might give a reduction effect on weight gain at OGTT in overweight pregnant women, but not obese pregnant women. However, we found no significant effects of MI on newborn outcomes. The majority of these outcomes had low occurrence rates and were seen in a limited number of patients. MI clearly showed the benefits in reducing GDM and improving maternal health. However, effect on neonatal health remains is still unclear, ti may be due to some limitations. There are many factors influence on the neonatal outcomes such as genetics, maternal health and environmental factors. Regarding the maternal/fetal outcomes, Valentina [34] highlighted that lower birth weight (p=0.043) and frequency of hypoglycemic events (p=0.001) were observed in women treated with MI compared to controls in their study.
The effect of probiotics as supplementation to prevent GDM was also analyzed. All six studies involving probiotics reported that there was no significant effect of probiotics on GDM occurrence. We identified three studies showed a reduction in GDM occurrence, but they did not differ significantly (Table 2). We also found three studies showed a reduction in all three glucose parameters which are FPG, 1-h and 2-h post load OGTT, but there was no significantly different except for study conducted by Asgharian [25] that reported significant reduction. When analyzing the probiotics strain used in these three studies, were both Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium subspecies. Thus, the probiotics that contains these strains do not reduce the GDM occurrence, but they may have potential effect on gut health and glucose metabolism. The study conducted by Ashgharian [25] started their intervention later compared to other studies which was at 24 weeks of gestation until delivery. We hypothesized that, if they started the intervention earlier which is at first trimester of pregnancy using the same strains with a larger population, probiotic would give a better result of effect as GDM prevention. As for maternal and neonatal outcomes, all studies reported no significant effect of probiotics on them. Though probiotics has potential in managing GDM by supporting healthy gut microbiome, improving glycemic control and enhancing insulin sensitivity, the larger number of studies are needed to conclude the effect of probiotics on maternal and neonatal outcomes.
There are some limitations in conducting this study. One notable limitation is potential inadequacy of available data. More studies are needed to provide more conclusive evidence on their effectiveness as supplement as GDM prevention. Another significant limitation is the challenge in drawing conclusions for secondary outcomes (maternal and neonatal outcomes) due to a small number of samples, or insufficient statistical power to detect meaningful effects for certain outcomes. Another noteworthy limitation is diversity of sample such as variations in population characteristics and varying baseline health conditions across the included studies which could affect the generalizability of the findings. Due to the inclusion of studies with diverse groups, such as overweight and obese pregnant women, women with a family history of type 2 diabetes, and women at highly susceptible for GDM, the effectiveness of the intervention may vary across different patients. Thus, the absence of uniformity in the available information and the restricted number of researches hinders the formulation of statistically significant findings for maternal and neonatal outcomes.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, myo-inositol can reduce the incidence of GDM, improve glucose metabolism and improve primary outcome. The review highlighted that myo-inositol significantly reduces the occurrence of GDM, which is a promising finding for its use as a preventive supplement. In terms of dosing, to prevent GDM with a dose of 4 gram plus 400 mg FA per day initiated at 12-13 weeks of gestation until delivery. However, the evidence for probiotics remains mixed based on the findings. While probiotics do not provide the strong evidence in preventive effects on GDM, however it may have potential effects on gut health and glucose metabolism in pregnant women when using lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium subspecies strains initiated at 12-13 weeks of gestation.
Further research could focus on larger, more diverse populations and explore the detailed mechanisms by which myo-inositol and probiotics effect glucose metabolism and GDM risk.
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :