-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Oluwaseye Adebajo*, Perpetual Adebajo, Honor Ojo, Oluwatobiloba Ayoade, Princess Ulasi, Michael Olajide and Lois Ajeseni
Corresponding Author: Oluwaseye Adebajo, Anatomy Programme, College of Health Sciences, Bowen University, Iwo campus, Iwo, Osun state, Nigeria.
Received: May 08, 2024 ; Revised: May 31, 2024 ; Accepted: June 03, 2024 ; Available Online: June 05, 2024
Citation: Adebajo O, Adebajo P, Ojo H, Ayoade O, Ulasi P, et al. (2024) A Role of Ascorbic Acid in Ameliorating Dextromethorphan-Induced Testicular Toxicity in Sprague-Dawley Rat Model. J Pharm Sci Drug Discov, 3(1): 1-8.
Copyrights: ©2024 Adebajo O, Adebajo P, Ojo H, Ayoade O, Ulasi P, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Background: Dextromethorphan (DM) is a cough suppressant, commonly abused among young adults. Ascorbic acid has been proved to have great ameliorative properties on the toxicity in the testes. Evaluating the effect of ascorbic acid on the testes of Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to dextromethorphan-induced testicular toxicity.
Objective: To evaluate the ameliorative potential of ascorbic acid on the seminal parameters (counts, motility, morphology) in Dextromethorphan-induced testicular toxicity in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Methods: Forty ats were used and divided into four groups (n=10) as follows: Group 1 received 0 mg/kg, Group 2-4: 20,40,80mg/kg of DM respectively for four weeks. Upon completion, 5 rats were randomly selected and euthanized from each group and the remaining animals received 100 mg/kg of Ascorbic acid for a period of four weeks. Upon completion, the rats were randomly picked and euthanized for histology on the testes, hormonal milieu parameter and oxidative stress.
Results: Dextromethorphan decreased rat testicular weight, inhibited spermatogenesis, decreased reproductive hormones and also induced oxidative stress which may cause a decline in reproductive function. Administration of Ascorbic Acid was able to restore reproductive functions.
Conclusion: The results showed that Dextromethorphan could affect reproduction function that can culminate into male infertility, amelioration was recorded upon administration of Ascorbic Acid as an antioxidant.
Keywords: Dextromethorphan, Ascorbic acid, Semen parameters, Oxidative stress
INTRODUCTION
The consequent abuse of cough suppressant containing Dextromethorphan is progressively becoming popular among young adult [1] as it is readily available as an over-the-counter medication and could be obtained via the internet from vendors of convenient stores. Numerous and countless factors have been disclosed to be liable for the hike in male fecundity [2] ranging from use and misuse of certain therapeutics, lifestyles consumptions and exposures to harmful chemicals. Ascorbic acid has been proved to have great ameliorative properties on the toxicity in the testes in various studies conducted, as shown in this report [3]. Dextromethorphan (DM)), has overtaken codeine as the most widely used cough suppressant due to its availability [4]. However, Dextromethorphan is subject to abuse and misuse. Since it is made available without a prescription, virtually anyone can get access to dextromethorphan merely by walking into a store [5]. Ascorbic acid has a potent antioxidant potential on the testes which is a pivotal component of the human male reproductive system and other vertebrates that plays crucial roles in reproduction and procreation. Ascorbic acid is known to strongly preserve the histological architecture and maintain the normal testicular functions. The antioxidant properties of ascorbic acid could protect the testes of the Sprague-Dawley rats against the hazardous impact of dextromethorphan [6].
Several researches as shown the alarming DM abuse statistics, it is evident that discussing more about its dangers is vital. Aside from the fact that it affects brain’s function to mention but a few, studies have shown that abusing dextromethorphan can lead to male fecundity.
The increasingly and constant use of this drug amongst young adults and aged individuals in Nigeria has been reported. This has initiated the ban on the sales of DM and/or cough suppressant containing DM over-the-counter [7].
Adequate and sufficient evidences from literature have unveiled the addiction and euphoria often derived when Dextromethorphan is used [8-10]. DM inhibit the secretion of gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus leading to a significant decrease with a deleterious effect on spermatogenesis [9,10], dysfunction of accessory sex organs, secondary sex organs, and impairment in sexual behavior [9,10]. A previous study had reported on the effect of chronic use of Dextromethorphan on fertility in male Sprague-Dawley rat [1]. Adebajo et al., reported that the administration of Dextromethorphan led to decrease in sperm count, motility, and normal sperm morphology, causes decrease in intra-luminal spermatozoa population and brings about oxidative stress in testes of Sprague-Dawley rats [1]. A previous study had reported that Dextromethorphan decreases seminal parameters while studying the role of Virgin Coconut oil on Dextromethorphan-induced testicular toxicity in Sprague-Dawley rat to reach a conclusive decision for remedies. In conclusion, we assumed these indexes would most definitely lead to a decline in fertility. This present study was structured to validate the claim and to proffer a solution to male infertility caused by Dextromethorphan-induced testicular toxicity in Sprague-Dawley rat model by studying the ameliorative potential of Ascorbic acid [11]. We also sought to determine and evaluate if the reported harmful effect of DM on the testes could be altered upon administration of Ascorbic acid as an ameliorative agent [12]. The experimental model (Sprague-Dawley) was chosen because it has similar structures to humans. The reproductive organs (for fecundity) in males are quite similar to that of humans. The spermatogenic cycles takes similar pattern from spermatogenesis to spermiation. Also, it takes a duration of 64 days in rats and 72 days in humans. The functions of reproductive hormones (FSH, LH and Testosterone) in both species are similar.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Drugs/ Substances
Dextromethorphan and Ascorbic acid were both purchased from Fairy Pharmaceutical Ltd., Zhuhai City, Guangdong Province, China.
Animal Model
Forty (40) male Sprague-Dawley rats, weighing between 160±40g were used. They were housed in a standard ventilated steel mesh plastic cages in the Animal House of the Anatomy Programme, College of Health Sciences, Bowen University, Iwo, Osun State, Nigeria. They were under standard room temperature and were left to acclimatize for a duration of two weeks before the commencement of the experiment. The method for administration of the substances (DM and Ascorbic acid) was orally. All experimental procedures and techniques were approved by the Health Research Ethics Committee of the College of Health Sciences, Bowen University, Iwo, Osun State, Nigeria, coupled with strict compliances with the guiding principles for research involving animal models [11].
Experimental Designs
Forty (40) male Sprague-Dawley rats were used and divided into four (4) groups (n=10) as follows: Group 1, served as control and received 0 mg/kg of Dextromethorphan (DM). Groups 2-4, served as low, medium and high doses received 20, 40 and 80 mg/kg of Dextromethorphan (DM) respectively for a period of 4 weeks [12]. The animals were randomly selected without bias into the respective groups. The doses chosen for this study were similar from previous study [12]. Also, a lethal dose (LD50) was conducted and the doses (therapeutic doses) were extrapolated from the it as 20, 40 and 80 mg/kg as low, medium and high doses respectively. Each animal has its own canula and the respective syringe. Also, error due to parallax was avoided.
Upon completion of each treatment routine, five (5) rats from each group were randomly selected and euthanized using 1 ml of Ketamine as anesthetic. The remaining 5 rats in each group were given 100 mg/kg of Ascorbic acid for another period of 4 weeks. Upon completion, the animals were sacrificed and their testes was obtained for histological findings and oxidative stress markers, blood was taken for hormonal parameters [13,14]. The testes were excised and seminal parameters were analyzed. The testes were fixed in Bouin’s fluid for histological purpose.
Histological Procedures
For the histological analysis, Hand E was used as stains. The sections were made at 5microns before photomicrography at X 400 magnification. The harvested testes were kept in a universal bottle containing Bouin’s fluid. Tissues were processed for microscopic examination making use of a standard protocol and 5µm thick paraffin section were made.
Testicular Weight
The testes were weighed using a sensitive weighing scale balance and recorded, before fixing in Bouin’s fluid.
Blood Collection
About 2mls of blood were collected through cardiac puncture into heparinized bottles. This were immediately put into the ice filled cooler, then into the refrigerator for preservation. The blood was later taken and centrifuged for about 20 min. After been separated from the red cells, it was stored in bottles and sealed before being put in the refrigerator.
Seminal Fluid Analysis
Incision was made on the caudal epididymis; it was then placed in a 0.5ml of 0.9% normal saline and fluid collected using a glass pipette. Epididymis fluid of 5ml was delivered into a glass slide and covered with a cover slip [15]. The sperm progressive motility was determined by Bearden and Fluquary [16]. The spermatozoa were also counted by hemocytometer, made use of the improved Neubauer chamber as explained by Pant and Srivastava [17]. Microscopic examinations of the seminal smears were stained with Eosin and the stains were carried out to determine the percentages of sperm the morphology (head, body and tail) [18]. The slides were viewed under a light microscope (MagX100).
Serum Hormone Analysis
Sera were obtained from blood sample collected and used for testosterone, follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone assays. The analysis was carried out using an enzyme-linked immunoassay (EIA) system. The EIA kits which contained the different EIA enzyme label, substrate reagents and quality control sample were obtained from Fortress Inc. (UK).
Statistics
The data acquired from all groups were compiled and statistically analyzed using One Way of variance (ANOVA) and Student t-test method on SPSS software version 22. LSD multiple test range was used to compare means obtained after each treatment with control measurements. The result of the data was expressed as mean ±SEM (standard error of mean) were p<0.05 was taken as significant.
RESULTS
Effects of Dextromethorphan and Ascorbic Acid on Body Weight of Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
In the Dextromethorphan group, significant increase was seen in the body weight of the adult male Sprague rats in both control and treatment groups. In the Ascorbic Acid group, significant increase was seen in the body weight of the rats in both control and treatment groups (Table 1).

Effect of Dextromethorphan and Ascorbic Acid on Testicular Weight
In the dextromethorphan group, an irregular pattern was recorded, slight increase was seen in both low and high doses and a decrease in medium dose when compared to control. When medium and high doses were compared to low dose, a slight decrease was noticed. Slight increase was seen when high dose was compared to medium dose. When treatment groups of Ascorbic acid were compared to the treatment groups of Dextromethorphan, slight increase in parameter was recorded (Table 2).

Effect of Dextromethorphan and Ascorbic Acid on Oxidative Stress Markers of Adult Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
In the Malondialdehyde (MDA) values of the Dextromethorphan group, when treatment groups were compared to control, significant increase was observed. In the Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and Catalase (CAT) values of the Dextromethorphan group, when treatment groups were compared to control, a significant dose-dependent decrease was recorded. However, when values of MDA in Ascorbic group were compared to the Dextromethorphan group, decrease in value was noticed as significant dose-dependent increase was recorded in the values of CAT and SOD when Ascorbic groups were compared to Dextromethorphan treatment group (Table 3).

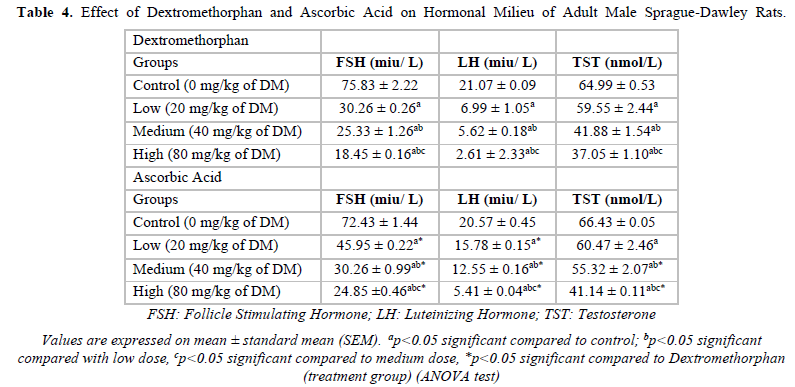
Effect of Dextromethorphan and Ascorbic Acid on Hormonal Milieu of Adult Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
In the Dextromethorphan group, when treatment groups were compared to control groups, a significant decrease was observed in the values of Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Testosterone however, when the treatment groups of Ascorbic acid were Dextromethorphan, significant dose-dependent increase in values were recorded (Table 4).
Effect of Dextromethorphan on Motility, Morphology and Count of Adult Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
In the Dextromethorphan group, decrease in seminal parameters was recorded when treatment groups were compared control, however, reverse was noticed as slight increase was recorded when treatment groups of Ascorbic acid were compared to Dextromethorphan group (Table 5).

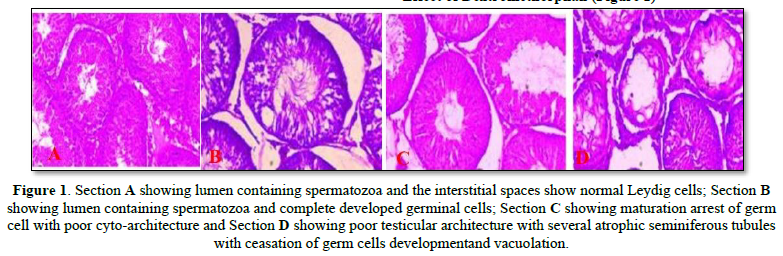
The Effects of Dextromethorphan and Ascorbic Acid on the Histology of the Testes of Adult Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
Effect of Dextromethorphan (Figure 1)
Effect of Ascorbic Acid (Figure 2)

DISCUSSION
This study was performed to firstly buttress the potential toxicity associated with Dextromethorphan as an antitussive in males and also determine the ameliorative potential of Ascorbic acid against Dextromethorphan-induced testicular toxicity in males. The decrease in testicular weight in the study may be due to low serum testosterone level, inhibition of spermatogenesis and decreased sperm production. There was a significant decrease in the mean levels of Superoxide dismutase (SOD) and slight significant decrease in the mean levels of Catalytic (CAT) in the treated animals. The reduction of the activity of Catalase (CAT) may reflect an inability to eliminate H2O2 produced by dextromethorphan due to enzyme inactivation caused by excess Reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in testis [19]. ROS cause damage to sperm and other cytoplasmic organelle membrane structures through peroxidation of phospholipids, proteins, and nucleolites, thereby altering sperm motility. However, impaired sperm motility may result in infertility due to the failure of sperm to reach the site of fertilization as well as their ability to penetrate zona pellucida. The observed increase in testicular Malondialdehyde (MDA) levels is a clear indication that dextromethorphan induces oxidative stress [20,21].
There was a significant decrease in seminal parameters in the treated group of dextromethorphan when compared to control. The significant decrease in sperm count recorded in all the treated group of dextromethorphan, strongly relates with the histological reports as seen in the photomicrographs in which there was decline in spermatozoa content in the seminiferous tubules. A slight decrease in the Serum Follicle-Stimulating Hormone levels was also observed. This also correlates with the result of the photomicrograph in which Sertoli cell function was preserved. The significant reduction in testosterone at all treatment dosages observed in the study supports the observed reduction in serum Luteinizing Hormone. Androgen deficiency disturbs the spermiation process by altering the spermatid-sertoli cell junctions, which results in premature detachment of round spermatids from sertoli cells and seminal epithelium [22]. Testosterone is known to be critically important in the development of sperm cells, and results in the Leydig cells dysfunction and testicular steroidogenesis disorder. It therefore follows that the observed decrease in sperm parameters may be due to the observed decreased levels of serum testosterone across all the treated groups. Reduction in both sperm count and motility, increase in abnormal sperm morphology and decrease in testicular weight produced by chronic administration of dextromethorphan are strong indicators of male infertility [2]. Infertility is defined as the inability of a male to achieve pregnancy in a fertile female.
The report of this present study therefore validates our previous claim that dextromethorphan causes male infertility [1-4]. After the administration of Ascorbic Acid to the treatment groups, there was a significant increase in count, motility and morphology when compared to control. There was a very slight significant increase in the mean levels of Malondialdehyde and slight significant decrease in the mean levels of Catalase and Superoxide dismutase in the treated animals. Hence, Ascorbic Acid reduced oxidative stress due to its antioxidant property. The serum Follicle-Stimulating Hormone levels were also observed to be slightly increased. This correlates with the result of the photomicrograph in which Sertoli cell function was preserved. The significant increase in testosterone at all treatment dosages observed in the present study is in concord with the observed increase in serum Luteinizing Hormone. Ascorbic acid deficiency has been linked to substantial degenerative alterations in the testes, epididymis, and vas deferens [23]. A lack of ascorbic acid may result in an increase in oxidative damage caused by ROS [24]. Ascorbic acid deficiency may cause infertility and promote damage to the genetic components of spermatozoa. There was an observed increase in Ascorbic acid levels in the treated groups compared to the control when antioxidant was administered. From this study, it was obvious that the antitussive-Dextromethorphan had deleterious effect on the parameters highlighted, however, ascorbic acid as an antioxidant was able to significantly improve spermatogenesis and reproductive parameters checked and this could possibly improve fecundity chances as this similar to reports from other researchers [25-28].
CONCLUSION
The therapeutic administration Dextromethorphan from this study has been established to have deleterious effect on the cytoarchitecture of the testes, hormonal milieu parameters (using Sprague-Dawley rats as models) and this could culminate into infecundity among (chronic/abusers) users. However, the administration of ascorbic acid (as an antioxidant) was able to restore the damaged reproductive functions. In lieu of this, we the authors discourage the abuse of Dextromethorphan; hence, it should not be sold as an OTC. In an advent of usage, Ascorbic acid can be administered to potential consumers of reproductive age so as to ameliorate the potential toxicity. Dextromethorphan decreased male rat testicular weight, inhibited spermatogenesis, decreased testosterone level and also induced oxidative stress which may cause a decline and inhibit reproductive function that could lead to infertility. Ascorbic acid was able to ameliorate the damage caused by Dextromethorphan thereby improving chances of fecundity. We recommend based on the findings from this study, that Dextromethorphan should only be made available strictly by prescription.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Authors declared no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We want to thank the entire members of non-academic staff of Anatomy Programme. We are grateful for allowing this research to be done in the laboratory. We are indeed grateful.
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :