-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Hephzibah Konadu Agyeman*, E O Darko, J Owusu-Banahene, B K Agyeman, A. O. Adukpo and Koffie L
Corresponding Author: Hephzibah Konadu Agyeman, Radiation Protection Institute, Ghana Atomic Energy Commission, P. O. Box LG 80, Legon-Accra, Ghana.
Received: February 23, 2022 ; Revised: April 6, 2022 ; Accepted: April 8, 2022 ; Available Online: May 1, 2022
Citation: Agyeman H K, E O Darko, J Owusu-Banahene, B K Agyeman, A. O. Adukpo et al. (2022) The Health Benefit of Sleeping and Related Sleep Disorders. J Ageing Rehab Res, 1(1): 1-4.
Copyrights: ©2022 Agyeman H K, E O Darko, J Owusu-Banahene, B K Agyeman, A. O. Adukpo et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Abstract
Rapid Eye Movement sleep occurs as blood flows through the arterial blood vessel, neuronal firing rates, and metabolism. This causes an increase in temperature in many parts of the central nervous system (CNS). However, REM sleep serves as a homoeothermic use to produce heat in order to maintain a high, stable temperature in a restricted central nervous system core during sleep. REM sleep is a regulated mechanism for warming the CNS. The “selection “of the brain network appears as a result of REM sleep. Mostly, Non-Rapid Eye Movement and Rapid Eye Movement sleep have contributed to the overall function of sleep. There is an alternation between Non-Rem and REM sleep which contribute to the overall function of sleep. Basically, the function of sleep is to provide “recovery” after proceeding waking activities, the recovery process comes as a result of interconnected neural network. and this aid in information processing, synaptic plasticity and cellular maintenance there by ensuring optimal functioning during subsequent wakefulness. If one of the functions of sleep is to conserve energy, then it is curious that energy is conspicuously expended in the vicinity of the central nervous system.
Keywords: Sleep apnea, Narcolepsy, REM sleep, Non - REM sleep, Obstructive Sleep Apnea, and Insomnia
INTRODUCTION
The brain is divided into three different categories these are as follows:
REM Sleep
Within the first 90 min of every sleep, REM sleep occurs immediately. At night, the sleep cycle occurs concurrently. REM sleep accounts for 20-25% in adults and 50% in infants [1]. The amount of REM sleep reduces when a person takes in alcohol before going to bed. The circadic rhythm is reduced by drockling effect which confuses the body internal clock. The effect of REM sleep has been linked to lack of sleep or sleep deprivation, which leads to a lack of defensive responses and coping mechanism in threatening situations. The National Sleep foundation have shown a profound benefit in association with REM sleep. When a person is unable to get enough REM sleep, he or she will find it difficult to remember what he/she was taught before going to sleep. Lack of REM sleep for four days can lead to cell profilation in the brain which aid in neural simulation and good memory mood [2,3].
NON - REM Sleep
This involves four stages; at the first stage the person falls asleep lightly. At the second stage, the person falls into a slightly deeper sleep. Finally, in the third and fourth stages which are also known as restorative sleep or delta sleep. Various activities take place during the NON-REM sleep such a, energy is replenished and stored, as well as the release of hormones. Moreover, there is also the repair of won out tissues and an increase in sexual arousement [4].
A research carried out in JAMA Neurology gave an indication that day time sleeping shows a sign of Alzheimer’s Diseases. One of the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease is noted with been sleepy during day time. Research says that genetic factors are one of the contributing factors of Alzheimer’s disease. It leads to robbing people of their memory which is known as a degenerative brain disorder (Figure 1).
Narcolepsy with cataplexy: The type of symptoms occurs when there is sudden muscle weakness and lose control of the muscles in their face, arms, legs, or torso.

Sleep Apnea
It is common in Germany and United States. Normally, there is a pause in breathing during sleeping. These pauses can last for a few minutes or seconds. During sleep apnea the brain and the rest of the body may not get enough oxygen.
Types of Sleep Apnea
There are three categories of Sleep apnea namely:
Characteristic of Sleep Apnea
Mechanism of Sleep Apnea
Difference Between of Central Sleep Apnea and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
In OSA, breathing is interrupted by a blockage of airflow (Figure 3).
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea occurs in various forms, but the most common among them is sleep apnea. It causes breathing to repeatedly stop and start during sleep. When a person’s throat muscles are intermittently relaxed and blocked the airway during sleep, a noticeable sign of obstructive sleep apnea occurs (Figure 3).

Central Sleep Apnea
Mixed Sleep Apnea
SLEEP RESTRICTIONS
SLEEP SOLUTION
BABY LULLABIES (Figure 4)

PREVENTIVE MEASURES
Positive Airway Pressure
Positive airway pressure (PAP) is usually, used a method to treat sleep apnea. It is an equipment that is use to pump air under pressure through. This is purposefully use to prevent airflow blockage (breathing) in people with obstructive sleep apnea (Figure 5).

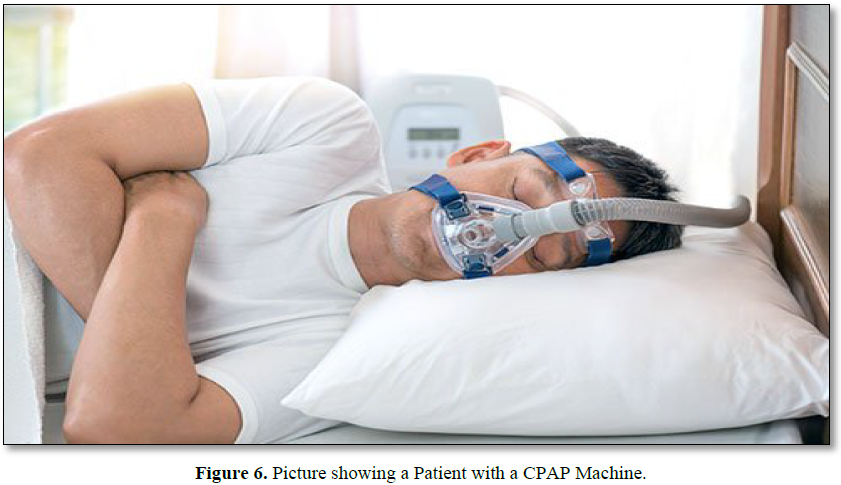
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy (CPAP)
This is an equipment developed to prevent air collapse during breathing in a person suffering from obstructive sleep apnea. Continuous positive airway pressure therapy (CPAP) is used to assist a person who have difficulty in breathing easily (Figure 6).
REFERENCES
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :