-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
K Subramanyam* and V Thirumala Rao
Corresponding Author: K Subramanyam, Principal, Sravanthi College of Education, Dharmaram, Warangal (Dt), Telangana, India
Received: January 20, 2022 ; Revised: March 02, 2022 ; Accepted: March 04, 2022 ; Available Online: April 30, 2022
Citation: K Subramanyam & Rao VT. (2022) Emotional Intelligence among College Students: The Role of Academic Stress and Self Confidence. J Psychol Psychiatr Res, 1(1): 1-5.
Copyrights: ©2022 K Subramanyam & Rao VT. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
The present study aimed to assess the impact of academic stress and self-confidence on emotional intelligence among college students.
Subject and Method: The researcher was mentioned research design, site of study, sample and tools used.
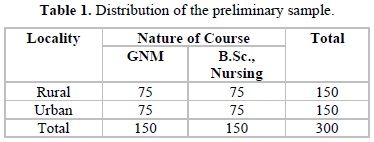
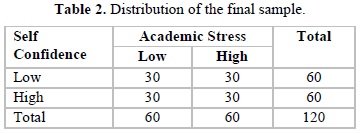
Sample: The sample of the present study consists of 120 nursing college students.
Tools: The emotional intelligence scale developed by Nutan Kumar Thingujam and Usharam (1999), students’ academic stress scale developed by Srinivas and Kumar Reddy (1999) and self-confidence inventory developed by Basavanna (1975) were administered.
Results: Students with low academic stress and good self-confidence have high emotional intelligence than the students with high academic stress and poor self-confidence.
Conclusion: There is a significant impact of academic stress and self-confidence with regard to emotional intelligence among nursing college students.
Keywords: Emotional Intelligence, Academic Stress, Self Confidence, Nursing Students
INTRODUCTION
The competence of nurses is based on the knowledge and skills that are taught to them; nursing training is a combination of theoretical and practical learning experiences that allow nursing students to acquire the knowledge, skills and attitudes to provide nursing care; Nursing training is made up of two complementary parts: theoretical training and practical training. A large part of nursing education takes place in clinical settings. Therefore, clinical education is considered an essential and integral part of the nursing education program since nursing is a performance-based profession, clinical learning environments play an important role in acquiring professional skills and training nursing students to enter the nursing profession and become registered nurses, the clinical area of nursing education is of great importance for nursing students in the selection or rejection of nursing as a profession.
In contrast to classroom training, clinical training in nursing takes place in a complex clinical learning environment that is influenced by many factors. This environment provides an opportunity for nursing students to learn experimentally and convert theoretical knowledge into a variety of mental, psychological and psychomotor skills important to patient care. Student exposure and preparation for entry into the clinical setting are one of the important factors influencing the quality of clinical education.
REVIEW
Montes and Berges [1] conducted a study on nursing students and the results showed that emotional information helps to reduce the negative stress problems. Therefore, this study will help the students to know about the academic stressors and how to manage the academic stress by emotional intelligence. Naidoo [2] showed that relationship between explanatory factors for stress and emotional intelligence. The ultimate aim of this survey is to compare perceived stress and emotional intelligence with respect to academic demands. The result concluded that less emotional intelligence is related with academic stress. Subburaj, Shunmuga Sundaram and Sekar [3] found that the role of emotional intelligence in managing academic stress. This result clears that academic stress variable significant predicator of emotional intelligence. Miri [4] concluded that there was no significant correlation between emotional intelligence scores and educational stress in students. Manasa Gomati, Bhagyalakhmi and Hemalatha [5] aimed the emotional intelligence and academic stress among adolescent boys and girls. Results revealed that there was no statistically significant difference of emotional intelligence and academic stress between boys and girls. Espinosa [6] found that the results showed self-confidence mediated such relation. Using moderated mediation SEM, the study also generalizes the results over summer versus regular semester students. The results suggest inclusion of trait EI within any mathematics curriculum will result in higher self-confidence among students. Kauts [7] designed to study academic stress and emotional intelligence among college students. Results indicated that students having high emotional intelligence has less academic stress than students with low emotional intelligence. Stevens [8] explored the relationship between emotional intelligence and academic stress among students at a small, private college. Private colleges’ students benefit significantly level of academic stress and emotional intelligence.
Montes and Berges [1] conducted a study in nursing students and the results showed that emotional information helps reduce negative stress problems, so this study will help students to understand academic stressors and how to manage academic stress through intelligence. Naidoo [2] showed that relationship between explanatory factors for stress and emotional intelligence. The ultimate aim of this survey is to compare perceived stress and emotional intelligence with respect to academic demands. The result concluded that less emotional intelligence is related with academic stress. Subburaj, Shunmuga Sundaram and Sekar [3] found that the role of emotional intelligence in academic stress management clarifies that academic stress is a significant predictor variable of emotional intelligence. Miri [4] concluded that there was no significant correlation between emotional intelligence scores and educational stress in students. Manasa Gomati, Bhagyalakhmi and Hemalatha [5] aimed the emotional intelligence and academic stress among adolescent boys and girls. Results revealed that there was no statistically significant difference of emotional intelligence and academic stress between boys and girls. Espinosa [6] found that the results showed self-confidence mediated such relation. Using moderated mediation SEM, the study also generalizes the results over summer versus regular semester students. The results suggest inclusion of trait EI within any mathematics curriculum will result in higher self-confidence among students. Kauts [7] designed to study academic stress and emotional intelligence among college students. Results indicated that students having high emotional intelligence has less academic stress than students with low emotional intelligence. Stevens [8] explored the relationship between emotional intelligence and academic stress among students at a small, private college. Private colleges’ students benefit significantly level of academic stress and emotional intelligence.
AIM
Emotional intelligence among college students: The role of academic stress and self-confidence among college students.
OBJECTIVE
To find out the impact of academic stress and self-confidence on emotional intelligence among nursing college students.
HYPOTHESES
POPULATION
Population for the present study consists of 1200 nursing students studying in different government and private colleges in Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh.
SAMPLE
From the population of 1200 students, a sample of 300 students from different colleges was selected randomly and administered “students’ academic stress scale, self-confidence inventory and emotional intelligence scale”. The subjects were in the age group of 18-21 years and using purposive sampling method. A final sample of 120 subjects was included in the present study as shown in the Tables 1 and 2.
VARIABLES STUDIED
In the light of the hypotheses formulated, the following variables are studied.
Dependent variable
Independent variables
TOOLS DESCRIPTION
RESEARCH DESIGN
As there are two independent variables i.e., academic stress (low and high) and self-confidence (low and high), each is divided in to two categories, a 2×2 factorial design was employed in the present study.
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
The obtained data was analyzed statistically in order to test the hypotheses using Means, SDs and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
A close observation of Table 3 shows that the students with low academic stress with good self-confidence obtained a high score of 123.81 indicates that they have high emotional intelligence compared to other groups. Students with high academic stress with poor self-confidence obtained a low score of 115.13 indicates that they have low emotional intelligence compared to other groups.
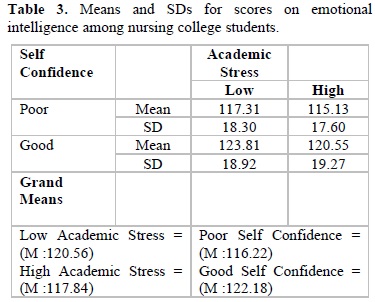
In terms of academic stress, students with low academic stress (M=120.56) have high emotional intelligence than the students with high academic stress (M=117.84). In terms of self-confidence, students with good self-confidence (M=122.18) have high emotional intelligence than the students with poor self-confidence (M=116.22).
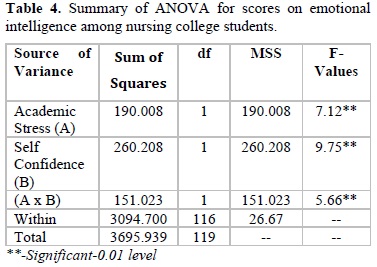
As there are differences in the mean scores with regard to the emotional intelligence among nursing college students, the data were further subjected to analysis of variance to find out the differences between the groups are significant or not, and the results are presented in Table 4.
HYPOTHESIS 1: THERE WOULD BE SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF ACADEMIC STRESS ON EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AMONG NURSING COLLEGE STUDENTS
It is evident from Table 4 that the obtained ‘F’ value of 7.12 is significant at 0.01 level indicates that academic stress has significant impact on emotional intelligence among nursing college students. As the ‘F’ value is significant, the hypothesis 1, which stated that academic stress has significant impact on emotional intelligence among nursing college students, is accepted as warranted by the results. Students with low academic stress (M=120.56) have high emotional intelligence than the students with high academic stress (M=117.84).
The results of the present study corroborate with the earlier findings of Montes and Berges, Naidoo, Subburaj, Shunmuga Sundaram and Sekar, Manasa Gomati, Bhagyalakhmi and Hemalatha, Deepa Sikand Kauts and Stevens [1-3,5,7] who stated that academic stress has positively and significantly related to emotional intelligence.
The result of the present study contradicts the findings of a study conducted by Miri [4] which reported that there was no significant correlation between emotional intelligence and educational stress in students.
The probable reason might be hundreds of emotions along with their combines and variations like anger, sadness, fear, enjoyment, surprise, disgust, shame and love etc. It's hard to learn all the emotions, but these entire emotions can learnable over a period of time all the way through environment. Students must possess the ability to choose to display or not to display their emotions. Emotions help to understand the situations in our daily life, using that students can able to handle situations positively. It includes self-control, persistence and enthusiasm to motive oneself. Evidence suggests that emotional intelligence is a key to managing academic stress and creating pleasant environment for the students and support them to present their best.
HYPOTHESIS-2: THERE WOULD BE SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF SELF-CONFIDENCE ON EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE AMONG NURSING COLLEGE STUDENTS
As shown in Table 4 that the obtained ‘F’ value of 9.75 is significant at 0.01 level indicates that emotional maturity has significant impact on mental health among nursing college students. As the ‘F’ value is significant, the hypothesis 2, which stated that emotional maturity has significant impact on mental health among college students, is accepted as warranted by the results. Students with good self-confidence (M=112.18) have high emotional intelligence than the students with poor self-confidence (M=116.22).
The results of the present study corroborate with the earlier findings of Espinosa [6] who stated that self-confidence has positively and significantly related to emotional intelligence.
The probable reason might be self-confidence works in opening doors as well as encouraging students to take risks and express their creativity in classroom affairs. A self-confident student is more likely to showcase optimistic and motivated attitude of learning and classroom affairs. With this understanding, the problem of low self-confidence may be approached differently by bringing the parents motivation into the picture. In general, high self-confident person perceives himself to be socially competent, emotionally mature, intellectually adequate, successful, satisfied, decisive, optimistic, independent, self-reliant, self-assured, forward moving, fairly assertive and having leadership qualities. So, only the students with high self-confidence can improves high emotional intelligence than the students with low self-confidence.
Table 4 clearly indicates that the ‘F’ value of 5.66 academic stress and self-confidence (AXB) is significant interaction at 0.01 level implied that there is significant interaction between academic stress and self-confidence is causing the effect on emotional intelligence among nursing college students.
CONCLUSIONS
There is significant impact of academic stress on emotional intelligence among nursing college students. Students with low academic stress have high emotional intelligence than the students with high academic stress.
There is significant impact of self-confidence on emotional intelligence among nursing college students. Students with good self-confidence have high emotional intelligence than students with poor self-confidence.
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :