-
Publish Your Research/Review Articles in our High Quality Journal for just USD $99*+Taxes( *T&C Apply)
Offer Ends On
Tanji Hoshi*, Mitsuhiko Morito and Tsutomu Sato
Corresponding Author: Tanji Hoshi, Tokyo Metropolitan University, 206-0013 Sakuragaoka 3-14-10, Tama-city Tokyo, Japan.
Received: August 21, 2024 ; Revised: August 27, 2024 ; Accepted: August 30, 2024 ; Available Online: September 16, 2024
Citation: Hoshi T, Morito M & Sato T. (2024) Comparative Analysis of The Causal Structure between the Presence or Absence of Family Physicians and Dentists in Older People and the Bedridden Status after Three Years. J Oral Health Dent Res, 4(2): 1-11.
Copyrights: ©2024 Hoshi T, Morito M & Sato T. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Views & Citations
Likes & Shares
Purpose: This research aims to examine the impact of the presence of a family physician or dentist on healthy longevity.
Methods: In September 2001, a self-administered questionnaire was conducted via mail among 16,462 elderly individuals in suburban Tokyo. The survey was repeated two times over six years, tracking the survival of 8,162 participants for three years (from 2004 to 2007). The study confirmed the dates of death for 278 men and 160 women.
Results: The study revealed that having only a family dentist was associated with a desirable socioeconomic status, favorable lifestyle and diet scores, and fewer treated diseases. Additionally, the presence of “Three Health Factors” was found to be preferable. The causal structure determining healthy longevity in relation to both survivals days and subjective health were clarified. Adverse effects on healthy longevity were observed in cases where only a physician was available. The influence of physicians and or dentists on healthy longevity accounted for approximately 44% of the role of socioeconomic status, 71% of healthy longevity could be explained.
Conclusion: This study emphasizes the importance of recognizing the role of family dentists in enhancing healthy longevity, as it is perceived to be more controllable compared to socioeconomic factors.
Keywords: Family physician, Dentist, Healthy longevity, Socioeconomic status
INTRODUCTION
Much more attention should be focused on healthy longevity in a rapidly aging country like Japan. Healthy longevity reduces the burden of long-term care and is linked to stabilizing medical and long-term care costs. Above all, it is significant that the person maintains a high quality of life and lives affluently [1]. Under these circumstances, Japan announced the Health Japan Plan 21 for healthy longevity in 2000 [2]. This plan clarifies the plan to maintain oral hygienic care, the basis of a rich diet, and measures to favor lifestyle-related habits, including smoking cessation. Family dentists play a central role in promoting desirable Oral Hygienic Care. The Japan Dental Association defines a family dentist as follows [3]. Dentists provide safe and secure dental care and have a wide range of knowledge and insights related to medical care; they can fulfill their responsibilities in regional medical care to maintain and improve oral function throughout residents' lives. On the other hand, family doctors play a significant role in preventing and treating various diseases, performing various health checkup activities, and improving lifestyle habits. The Japanese Medical Association defines a family doctor as a home medical doctor who can discuss health-related and refer patients to a specialized medical institution when necessary [4]. The Japan Dental Association has released a report outlining the scientific evidence supporting dentists' role in promoting dental and oral health to advance a society with longer life spans. The report, titled "Evidence for Dental Health and Oral Health that Contributed to a Healthy and Longevity Society in 2015," includes a follow-up study indicating that women with ten or more remaining teeth tend to have better survival rates [6, 7]. Additionally, the report highlights a significant reduction in the incidence of aspiration pneumonia in institutional residents who received oral hygiene care compared to those who did not, resulting in a lower mortality rate among the group receiving intervention [7].
In a study examining the connection between having a family dentist and overall survival, researchers monitored the survival rates of 16,462 older adults in suburban areas over six years. The study found that men and women with a family dentist had significantly higher cumulative survival rates than those without. Furthermore, when other relevant factors were considered using the Cox proportional hazard model, the study reported that women with a family dentist experienced significantly better maintenance of survival days [8].
Even if a family has access to a dentist and survives, it is still being determined how socioeconomic factors, lifestyle habits, and three health factors are causally related. The significance of having access to only a dentist for promoting healthy longevity can be estimated based on socioeconomic factors, the causal relationship with positive lifestyle habits, and the benefits of the three-health status.
This study explores the connection between older individuals in the suburban area of Tokyo and their family doctors or dentists, as well as their socioeconomic status, physical, mental, and social health, disease status, and lifestyle. Furthermore, the study aims to establish the causal structure of healthy longevity as a dependent variable associated with subjective health status after three years and the projected lifespan for the next three years based on gender. If the hypothesis of this research is confirmed, it is anticipated that the significance of having access to only a family dentist, a controllable factor, will increase.
Research Subject
In our study, we conducted a six-year cohort survey to track survival rates among older individuals living in suburban Tokyo. In September 2001, we distributed a questionnaire to all elderly individuals aged 65 and over who lived at home in Tama City, Japan. Of 16,462 eligible participants, 13,066 (79.4%) agreed to participate and completed the questionnaire. In September 2004, we sent a follow-up questionnaire to the same participants. 8,558 individuals responded, while 505 had moved, 914 had passed away, and 3,218 did not respond. We continued to track all participants until August 31, 2007. Our analysis included 8,162 subjects, consisting of 3,851 males and 4,311 females aged 65 to 84 at the start of the study. Over the three years from 2004 to 2007, we confirmed the death dates of 278 men and 160 women through the municipal resident registry.
Research Area
The research area for this study is a city that grew in the 1970s to 1990s as a commuter town to accommodate an increasing number of workers and their families in the metropolitan Tokyo area. This period coincided with a time of high economic growth in Japan. The majority of residents were middle class. In 2000, the city's total population was 145,862, with 11.1 percent being 65 or older.
The Questionnaire and Measures
In the questionnaire surveys, standardized questions were used to assess health status and lifestyle. We included questions about family physicians and dentists to differentiate between the two.
Socioeconomic status in 2001 was measured by educational attainment and annual income. Educational attainment was classified into four groups: completion of senior high school, completion of junior college, achievement of a higher academic level than college, and those who chose not to respond.
In 2001, income levels were divided into four categories: less than one million Japanese yen (equivalent to less than US $7,142), less than three million yen, less than seven million yen, and more than seven million yen.
As a variable to observe socioeconomic factors, we included educational background, annual income, and height. Height is considered an indicator of a prosperous and healthy childhood. It has been reported to be a valid indicator of survival prognosis after about half a century.
According to Jousilahti [9], a follow-up study was conducted on 31,199 adult residents in East Finland over 15 years, which found that shorter height increased the overall mortality rate. Similarly, a study followed 13,460 older adults in our country's suburbs for three years. The results showed that the mortality rate of males with a BMI of less than 19 and females with a height of less than 150 cm was significantly higher than that of the taller group [10].
Our research focused on the World Health Organization's definition of health, which includes physical, mental, and social well-being. For physical health, we used the basic activities of daily living (BADL) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL) as measured during a 2001 survey [11,12]. The BADL score was determined based on three questions: "Can you go to the toilet by yourself?", "Can you take a bath by yourself?" and "Can you walk outside?". Each function a person could perform earned them one point, with scores ranging from 0 to 3. Higher scores indicated greater basic activity competence. The IADL score was calculated using five questions related to instrumental activities: "Can you buy daily necessities by yourself?", "Can you cook daily meals by yourself?" "Can you deposit and withdraw money in a bank account?" "Can your complete documents related to insurance and pensions?" and "Can you read books and newspapers?". Like the BADL, the IADL score ranged from 0 to 5, with higher scores reflecting more excellent proficiency in instrumental activities.
Mental health was self-reported as subjective health during the 2001 and 2004 surveys. The question asked was, "Do you think you are healthy?" and had four response options: very healthy, moderately healthy, not so healthy, and unhealthy [13]. In the 2001 survey, the question measured life satisfaction, "Are you satisfied with your daily life?" with three response options: very satisfied, moderately satisfied, and unsatisfied. The scores ranged from 1 to 3 [14].
Social health was measured by examining how often participants went outside and communicated with their neighbors. Participants were asked, "How often do you go outside?" with response options including less than once a month, more than once a month, and more than 3 to 4 times a week [15]. Communication with the neighborhood was assessed by asking, "How often do you communicate with your friends or neighbors?" with response options ranging from seldom, once a month, 3 to 4 times a week, and almost every day, using a scale from 1 to 4 [16,17].
The study considered certain habits as healthy lifestyle choices based on their significant association with the number of survival days six years later. The habits that showed a significant association with increased survival days were alcohol consumption almost every day, never smoking (not even in the past), getting less than nine hours of sleep per night, exercising more than once a week, and having a BMI of more than 20. These healthy lifestyle habits were scored from 0 to 5, with a higher score indicating a healthier lifestyle [15,17].
Based on the follow-up survey, our analysis revealed a set of healthy dietary habits as follows: consumption of meat, eggs, and blue-backed fish 1 to 4 days a week; consumption of soy foods, dairy products, and fruits more than three days a week; consumption of vegetables more than five days a week, and having breakfast every day. Subsequently, a dietary health score was calculated based on the consumption of the four identified healthy dietary food categories (three points for each type), ranging from 0 to 12, with a higher score indicating healthier nutritional habits [18].
The prevalence of diseases significantly associated with a decreased survival rate over six years was summarized based on the number of treated diseases. The five diseases included hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, heart disease, and liver disease. The number of diseases being treated ranged from 0 to 5 points.
The study assessed the number of days elderly individuals survived over three years, starting in 2004, to assess their survival rate. In September 2001, the level of being bedridden was used as an indicator of elderly health, using a public assessment tool created by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. This tool has six levels, from requiring mild support to needing comprehensive care. In our analysis, respondents who received no care were scored as zero, while those needing minor support were scored as one, and those requiring the most care were scored as six. The "healthy longevity" (“ ” means Latent variable) was defined as a latent variable using the number of days survived over three years and self-reported health status three years later as observation variables.
Privacy
The Tama City local government and the Tokyo Metropolitan University have signed an agreement regarding protecting privacy and confidentiality. Mutual confidentiality is strictly enforced, and all analysis data is supported only by ID. The survey was conducted on September 16, 2000, with the consent of the Tokyo Metropolitan University Graduate School of Ethics Committee.
Data Analysis
The data was analyzed using IBM's Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) and AMOS Version 27 software. The relationship between categories was determined using the chi-square test or the Kendahl τ test, and quantitative comparisons were made using a one-way analysis of variance. Covariance structure analysis was utilized to clarify the causal structure of the hypothetical model with latent variables. The latent variables used in the model were determined through exploratory factor analysis by varimax rotation using the maximum likelihood method. In the causal structure analysis, the goodness-of-fit index of the model was evaluated using NFI (Normed fit index), 1FI (Incremental fit index), and RMSEA (Root mean square error of approximation) [21,22]. All estimates were standardized constants; a statistically significant difference was considered 5% or less.
RESULTS
Analysis targets number
Table 1 shows the gender and age group of the subjects. Eight thousand one hundred sixty-two subjects, aged 65 to 84, were analyzed: 3,851 men and 4,311 women. In the previous study [21,22,23], the distributions of all variables used in this study except for the family physician and dentist by sexes were described in detail.
Classification method of physicians and dentists
The classification method for physicians and dentists is as follows: 60.6% of individuals have both a physician and a dentist, 17.2% have only a family physician, and 12.7% have only a family dentist. The percentage of individuals with only a family physician increases significantly with age, while the proportion of individuals with only a family dentist decreases significantly with age. Additionally, 938 people (11.7%) were uncertain whether they had a physician or dentist.
The related factors with family physicians or family dentists
Our analysis examined the relationship between the survival duration and the presence of family physicians and dentists. We classified the data into four groups based on survival duration. The most extended survival was associated with having only a family dentist, followed by the group with no family physician or dentist. The group with family physicians and dentists had a moderately long survival, while the shortest survival was observed in the group with only family physicians. For individuals with only a family dentist, the three-year survival was 1,042.9 days for men and 1,054.7 days for women, whereas for those with only a family physician, it was 1,028.1 days for men and 1,036.7 days for women (Table 1).
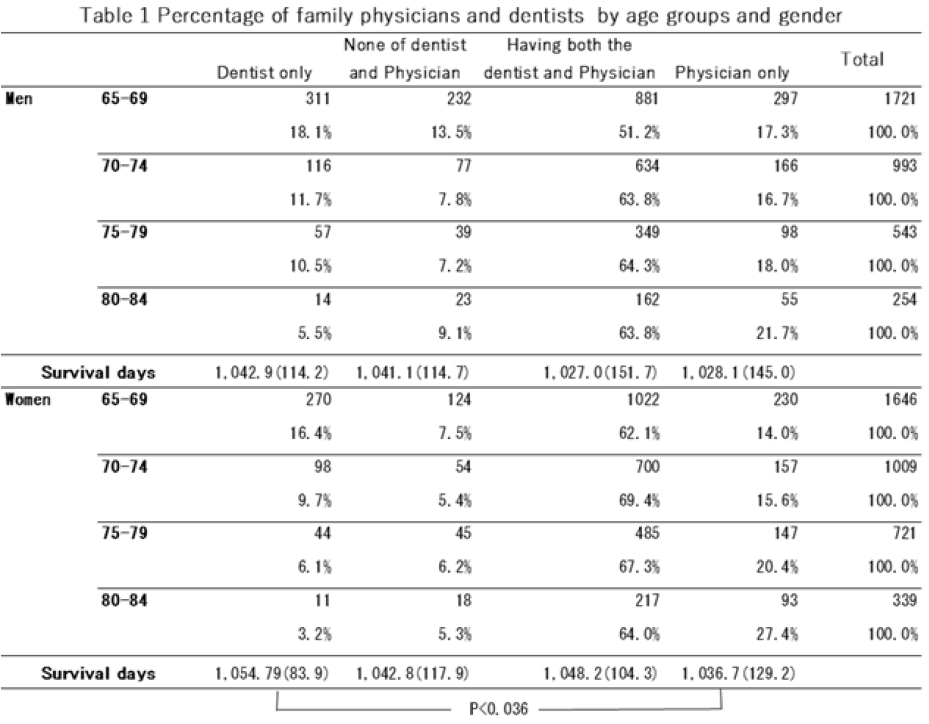
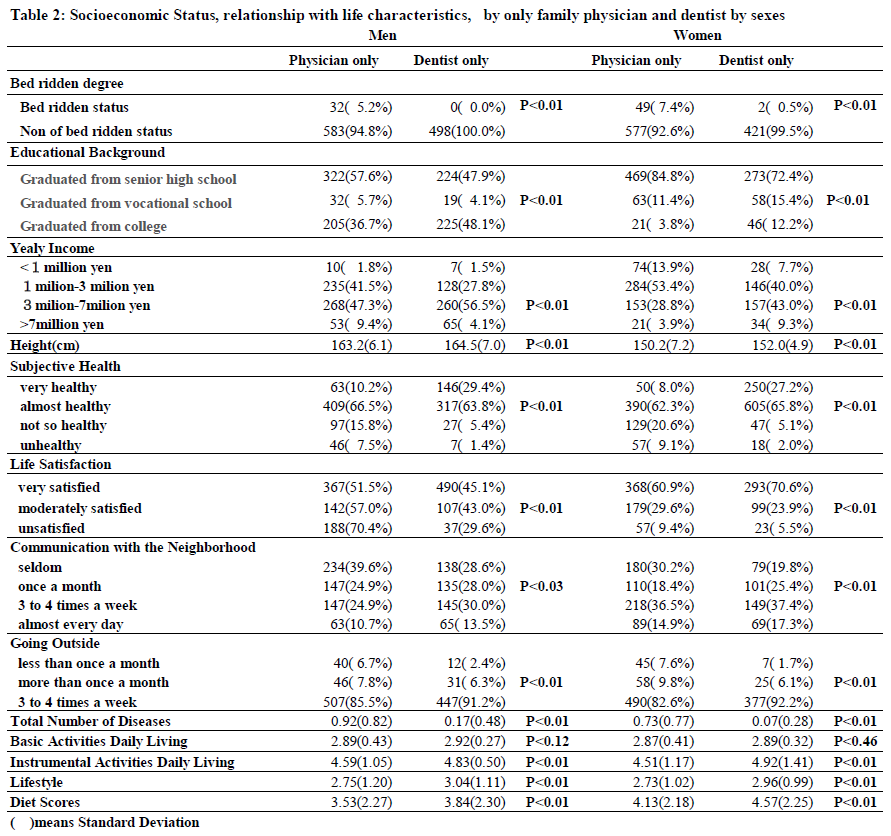
The group with only a family dentist showed significant associations with survival duration and subjective health, except for BADL, compared to the group with only a family physician. There was no clear association between the group with both a family physician and family dentist and the group with neither. We further compared the relevant factors for the groups with only a family physician and only a family dentist, categorized by gender (Table 2).
Causal structure with various factors for healthy longevity
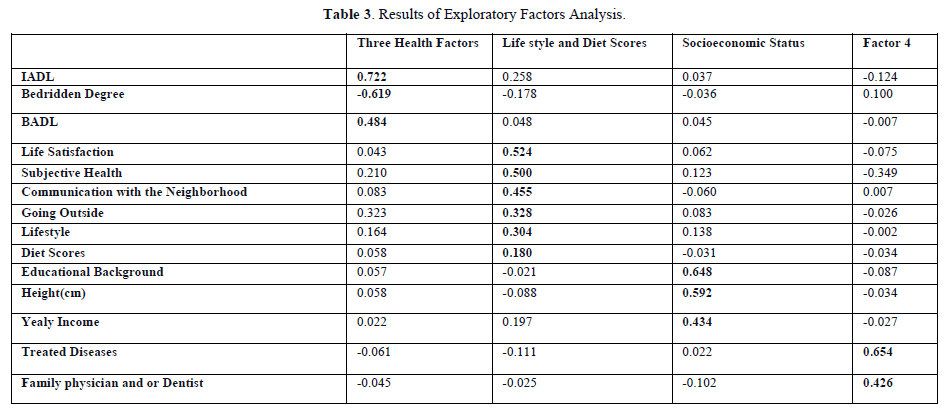
Results of Exploratory Factor Analysis
In the exploratory factor analysis, we used the maximum likelihood procedure and a Promax oblique rotation to identify latent variables. The results showed that the first factors were IADL, Bedridden Status, and BADL. The second factor included Life satisfaction, Subjective Health, Going outside, Communication with the Neighborhood, Lifestyle, and Diet scores. The third factor comprised Educational Background, Yearly Income, and Height, collectively named "Socioeconomic Status." The observational variables of the first and second factors, excluding "Lifestyle" and "Diet Scores," were combined to form the "Three Health Factors." The fourth factor included Physicians and/or Dentists and Treated Diseases. The cumulative sum of squared loads for the three health factors was 30.7%, and the Cronbach's Alpha Confidence Coefficient was 0.98 for the "Three Health Factors" and 0.38 for "Lifestyle" and "Diet Scores." However, the "Socioeconomic Status" factor had a low coefficient of 0.15 (Table 3).
Structure relationship for healthy longevity
To establish a relationship for healthy longevity, we used hypothetical models based on latent variables obtained through exploratory factor analysis. We searched for the model with the best fit using a modified index. In addition to "Healthy Longevity," we also surveyed items such as "Socioeconomic Status," "Lifestyle Diet Scores," the "Three Health Factors," and Treated Disease and Physicians and/or Dentists simultaneously. Each survey item could be a cause or effect at the same time. To clarify causality, we examined all combinations' direction and strength of cause and effect. For instance, if only dentists are selected, it is estimated that the three health factors are desirable based on the advisable "Socioeconomic Status."
On the other hand, due to the superiority of the "Three Health Factors," there may be fewer diseases, and they will choose a dentist instead of a physician. Therefore, we examined the causality of all combinations and selected the one with the larger standardized estimate. As a result, we positioned "Healthy Longevity" as a dependent latent variable using "Socioeconomic Status," "Three Health Factors," and "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" as explanatory latent variables, including both Treated Diseases and Physician and/or Dentist as an explanation observed variable. The reason why the path is not drawn indicates that no significant difference was found.
The goodness-of-fit index NFI was 0.795, IFI was 0.802, and RMSEA was 0.037. Because there was a high degree of conformity, the final structure diagram based on the literature [21,22] was adopted. All effects on the dependent variable were based on standardized coefficients. Additionally, we looked for direct and indirect effects through one or more factors and determined a total effect that combined direct and indirect effects. Moreover, all relationships between latent and observed variables were significant in the Wald test.
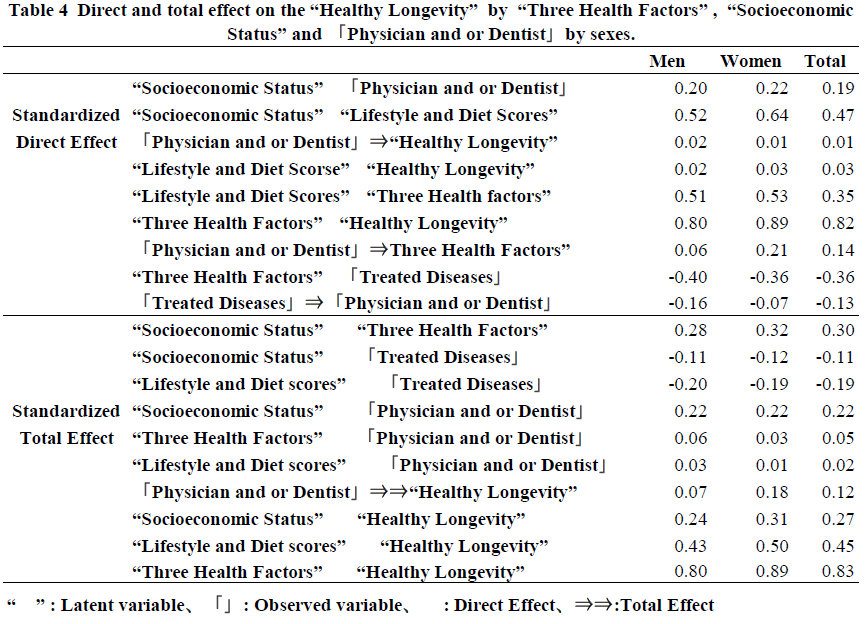
"Lifestyle and Diet Scores" and Physicians and or Dentists and Confounding Factors on "Healthy Longevity" In the analysis presented in Figure 1, the direct impact of "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" and 「Physicians and or Dentists」(「」means observed variable) on "Healthy Longevity" was found to be minimal (0.01 and 0.03, respectively). The relationship between "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" and "Healthy Longevity" was shown to be confounded by "Three Health Factors" and "Socioeconomic Status," with a significant association of 0.82 in the simple relationship. Additionally, the low number of「Treated Diseases」associated with "Socioeconomic Status" made it more likely to select only dentists rather than family physicians. Furthermore, "Three Health Factors" were found to play a crucial role in determining "Healthy Longevity." Although the direct impact of「Physicians and or Dentists」on "Healthy Longevity" was less than 0.01, the overall effect was 0.12, accounting for approximately 44% of the role of socioeconomic status. The variables explained seventy-one percent of "Healthy Longevity" (Figure 1). In the next step, we will describe the relationship between each observed variable, latent variable, and "Healthy Longevity."

Relationship between the「Physician and or Dentist」and other factors
The direct effect of "Socioeconomic Status" on the use of「Physicians and or Dentists」was 0.19, while the direct effect of「Treated Diseases」was -0.13. This suggests that individuals with higher "Socioeconomic Status" who only use family dentists tend to have fewer diseases to treat. The direct effect of using「Physicians and or Dentists」to the "Three Health Factors" was 0.14, indicating that having a family dentist is associated with maintaining physical, social, and mental health. However, the determination coefficient for selecting「Physicians and or Dentists」was only 7%, meaning that 93% of the factors remain unknown.
Relationship between "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" and other factors
The direct effects of "Socioeconomic Status" on "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" was 0.47, explaining 22% of the determination coefficient of the "Lifestyle and Diet Scores."
Relationship between "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" and "Three Health Factors”: The direct effects of "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" on the "Three Health Factors" was 0.35. The indirect effects of "Socioeconomic Status" on "Three Health Factors" through "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" was 0.16 (calculated as 0.47 multiplied by 0.35), explaining 22% of the determination coefficient of the "Three Health Factors."
Relationship Structure with Treated Diseases and other factors
The direct effect of the "Three Health Factors" on Treated Diseases was significantly negative at -0.36, explaining 14% of the determination coefficient of Treated Diseases which indicates that the favorable "Three Health Factors" substantially impacted reducing Treated Diseases.
Total Effects of Explanatory Factors on "Healthy Longevity"
The impact of various factors on "Healthy Longevity" was examined. The "Three Health Factors" had the most significant direct effect at 0.83, while the direct effect of "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" was 0.03. Additionally, the total effect of "Socioeconomic Status" was 0.27, indirectly influencing "Healthy Longevity." It was found that "Socioeconomic Status" indirectly affects "Healthy Longevity" by promoting "Lifestyle and Diet Scores," controlling the "Three Health Factors," and preventing 「Treated Diseases.」Although the direct effect of「Physician and or Dentist」on "Healthy Longevity" was small at 0.01, their total effect via the "Three Health Factors" was estimated to be 0.12, which accounts for 44% (0.44=0.21/0.27) of the total effect of "Socioeconomic Status."
DISCUSSION
The Causal Effect of Having Only a Family Dentist and Healthy Longevity
The findings of this study indicate that having only a family dentist has a small direct effect on "Healthy Longevity." However, by reducing the occurrence of diseases that a family dentist can treat and by promoting desirable lifestyle and diet scores based on socioeconomic status and three health factors, it becomes easier to rely solely on a family dentist rather than a physician. This connection to maintaining "Three Health Factors" contributes to preserving "Healthy Longevity." The study's novelty lies in the revelation that the overall effect of Physicians and or Dentists accounts for 44% of the total effect of "Socioeconomic Status." Based on the prior study, having a family dentist increases survival after six years [9]. This new research elucidated the causal structural relationship between "Socioeconomic Status," the "Three Health Factors," and the "Treated Diseases." It is suggested that the influence of having only a family dentist on healthy longevity should not be interpreted without considering the overall basic effect of socioeconomic factors, the desirability of lifestyle and dietary habits, and the reduction in the number of diseases to be treated after maintaining the three health factors. The role of family dentists in determining healthy longevity should be given more attention, as it is considered more controllable compared to the difficult-to-control socioeconomic factors. Previous studies [9] have not reported a relationship between having only a dentist and socioeconomic factors, so further research is needed to confirm these findings.
On the other hand, the group that only had a family doctor negatively impacted healthy longevity. This study suggests that the overall impact of treating more diseases was overlooked due to unsatisfactory socioeconomic factors, unhealthy lifestyle habits, an unfavorable diet, and undesired three health factors. It was also found that socioeconomic factors and the three health factors were influencing factors in maintaining healthy longevity due to lifestyle habits and dietary preferences. In other words, achieving healthy longevity isn't solely due to desirable lifestyle habits and diet but because favorable socioeconomic factors can lead to preferable lifestyle habits. This study reconfirms previous research findings [23]. Additionally, the final model explains seventy-one percent of "healthy longevity."
Importance of the Three Health Factors for the Total Effect on Healthy Longevity
The "Three Health Factors" had the most significant overall effect on "Healthy Longevity" at 0.80 to 0.89, followed by "Lifestyle and Diet Scores" with a total effect of 0.43 to 0.50. The total effect on "Healthy Longevity" from "Socioeconomic Status" is 0.24 to 0.31. Although "Socioeconomic Status" does not directly affect "Healthy Longevity," it is an essential foundational factor. Additionally, educational background, a socioeconomic factor, is linked to a decrease in disease prevalence and the maintenance of the ability to live actively, along with the maintenance of the three health factors, contributing to extended healthy longevity. When the dependent variable, the number of days to live, was analyzed only by the observed variable, the coefficient of determination was as low as 8%.
The coefficient of determination for the analysis of subjective health alone was 53%. The study suggested that "Healthy Longevity," as defined in this paper, is a latent variable emphasizing subjective health perceptions. Among all the explanatory variables, subjective health was found to be the most strongly associated factor with subjective health after three years, as well as with the dependent variable, the number of days to live after three years. Previous reports have indicated that subjective health is a highly valid indicator of survival [15,18]. It's also worth noting that the group with only family dentists consistently maintained subjective health.
The actual situation of Physician and or Dentist
Our study found that 17.2% of older people living in suburbs only had an internal physician, and this percentage increased with age. On the other hand, 12.7% of older people only had a family dentist, and this percentage decreased with age for both sexes. The study suggests that as people age and their educational attainment and yearly income decline, they may require more medical treatment, increasing the number of people relying solely on family physicians. Previous research on the situation of family dentists has only been reported by the Japanese Dental Association. According to a nationwide survey conducted by the Japan Dental Association in 2011, 77.7% of people in their 60s and 87.7% of people in their 70s have family dentists. Investigating the proportion of people who only have a family dentist soon is essential.
The importance of having a family physician and a dentist Previous studies have highlighted the importance of family dentists and dental hygienists in delivering thorough and systematic oral hygiene care for individuals. This care includes primary, secondary, and tertiary preventive measures, as evidenced by researchers such as Ogden [24] and Kaneko [25]. The significance of oral hygiene care is linked to overall health, especially regarding eating habits. Research by Gellrich [26] emphasizes the early detection of illness and the promotion of healthy lifestyles by dentists. Similarly, Reichart [27] advocates for the utilization of the "four A" strategy (Ask, Advice, Assist, and Arrange) for disease prevention, which aligns with the EU Europe's preventive strategy model. Furthermore, a study by Takada [28] demonstrates the positive impact of dental examinations and health education provided by dental hygienists. The research by Takada et al. shows a significant decrease in the rate of suspected periodontal disease in men following these interventions. The research suggests that having a family dentist and receiving oral hygiene care is associated with better health outcomes and longevity. Focusing on preventive activities and maintaining good oral hygiene habits is recommended, as these can contribute to disease prevention and overall well-being. The research also highlights the importance of visiting a family dentist for preventive care rather than solely for treatment, as it can positively impact long-term health and survival.
Further studies are needed to explore the causal relationship between visiting family dentists and subsequent healthy longevity, including the motivations for preventive dental visits and diagnosing oral hygiene issues. Collaboration between family physicians and dentists Extensive research reviews have shown that the support of family physicians reduces health risks and improves survival rates. By April 2021, 22,099 research papers on the relationship between risk factors for diabetes, hypertensive disease, and subsequent mortality were reviewed. This meta-analysis demonstrates that the core medical activities of family doctors help control diseases and mortality risk factors, ultimately contributing to improved survival [29]. Therefore, it is essential to replicate scientific evidence, like our study, to show that survival rates were maintained in groups with only family dentists and no family physicians. Oral infections such as tooth decay and periodontal disease are risk factors for infectious endocarditis. Yamada et al. (30) emphasized the importance of addressing oral infections through dental care, in coordination with medical examinations, before surgery for congenital heart disease to highlight the need for collaboration between medical and dental care.
Future research issue
The causal structure of this survey only discusses the impact on "Healthy Longevity" after three years. The survey period for the "Three Health Factors" aligns with the survey period for "Socioeconomic Factors" and "Physicians and Dentists." The next step is to clarify the causal structure through follow-up surveys conducted over different years for all latent variables. It is also a research priority to validate the findings with representative subjects and enhance external validity. Furthermore, the following study should analyze the causal structure of healthy longevity after clearly defining the oral hygiene diagnosis made by the dentist, including objective indices, alongside medical examinations.
This study revealed a causal structure in which socioeconomic factors were favorable, indicating that individuals who tended to have only family dentists experienced healthy longevity. However, the independence and self-efficacy of individuals with a family dentist remained unclear. It is also necessary to clarify the type of oral hygiene care undertaken in collaboration with the patient's dentist. Subsequent studies on other populations have demonstrated that those more inclined towards preventive dental care and preferred self-care for oral hygiene, in conjunction with dentist support, exhibited improved subsequent oral hygiene status and were associated with maintaining their subsequent survival [31]. In the future, the research should focus on clarifying the emphasis on prevention with family dentists and the preventive and therapeutic effects of oral hygiene on both the patient and the specialist.
CONCLUSION
The study found that the relationship between having only a dentist instead of a physician and "Healthy Longevity" was primarily influenced by "Socioeconomic Status." Moreover, favorable "Lifestyle and Diet Scores," excellent "Three Health Factors," and prevention of treated diseases were also associated with "Healthy Longevity." While "Three Health Factors" and "Lifestyle and Dietary Scores" had a significant impact on "Healthy Longevity," "Socioeconomic Status" was identified as the fundamental element. The study suggests that the total effect of having "Physicians and or Dentists" on "Healthy Longevity" accounts for 44% of the total effect of "Socioeconomic Factors" and should be considered a controllable factor. The study underscores the significance of acknowledging the impact of family dentists on promoting long-term health, which is more manageable than enhancing socioeconomic factors. The research emphasizes the necessity of reproducibility in future studies.
No Files Found
Share Your Publication :